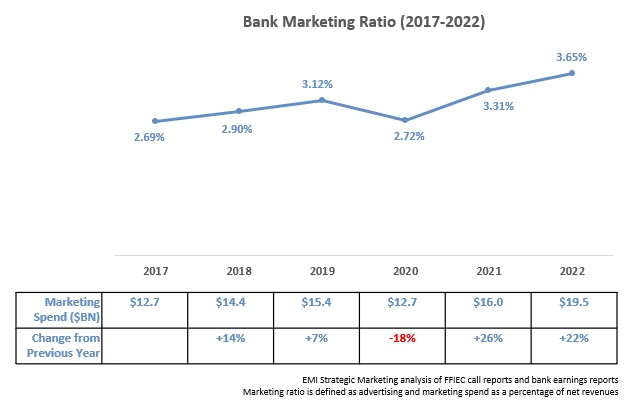
An EMI Strategic Marketing analysis of 30 leading U.S. banks found strong overall growth in marketing budgets for the second consecutive year. Following an 18% decline in 2020 in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, these leading banks have grown their marketing budgets by 53% over the past two years.
Five banks – American Express, Capital One, JPMorgan Chase, Citi and Bank of America – each spent more than $1 billion in advertising and marketing in 2022. Discover was just below this threshold.
These banks’ average marketing ratio (marketing spend as a percentage of net revenues) rose by 34 basis points (bps) to 3.65% in 2022.
There is significant variation in bank marketing ratios between – and within – different banking categories.
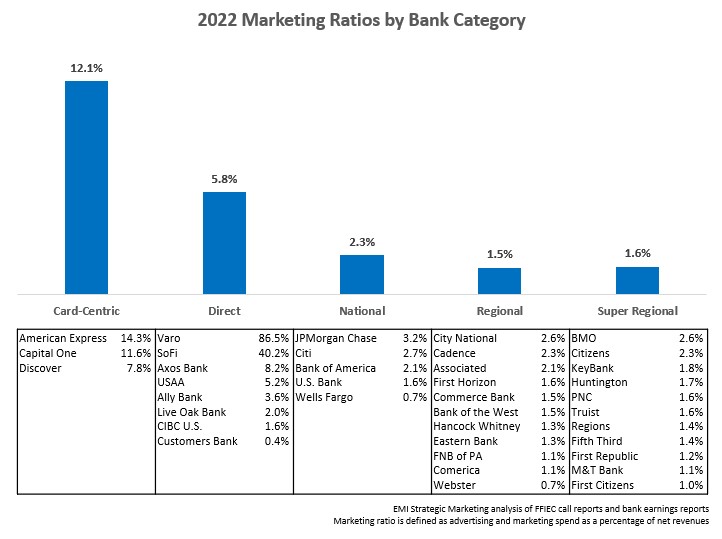
- Card-centric banks like American Express and Discover tend to have high marketing ratios as they have national reach but no branch networks.
- Direct banks also have relatively high marketing ratios as they lack branch networks. Newer challenger banks are also investing significantly in marketing to build customers, deposits and assets.
- More ‘traditional’ bricks-and-mortar banks typically have marketing ratios in the 1-3% range, although even in these categories we see significant variation as individual banks pursued different marketing objectives. Regional banks like Cadence Bank (+285% to $42 million) and BMO (+23% to $128 million) ramped up budgets in 2022 to promote brand overhauls. Super regional banks like Citizens (+38% to $184 million) and M&T Bank (+41% to $91 million) significantly grew their marketing spend to support entry into new markets following recent acquisitions.
Going into 2023, the projected trajectory for bank marketing spend is less clear, with rising inflation and slowing economic growth forcing banks to look for ways to reduce expenses. In addition, because they have grown budgets in recent years, some leading banks may decide to pause or even scale back their marketing budgets in 2023. However, many have stated their commitment to maintaining or even growing their marketing investment to support specific business strategies.
- Discover expects double-digit growth in marketing spend as it pursues growth opportunities in credit card and deposits. It also claims that it continues to see strong returns on its investments.
- Fifth Third plans to increase marketing spend in the mid-single digits in 2023 as it targets customer acquisition in the Southeast.
- Axos Bank is maintaining higher spend levels as it seeks to grow deposits in an increasing competitive market.