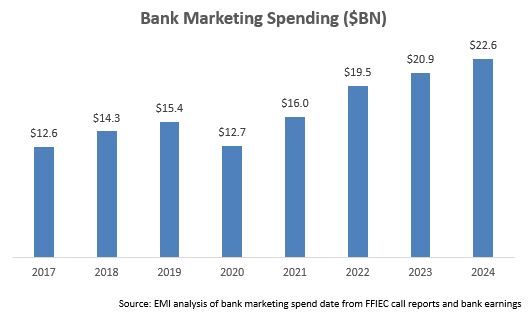
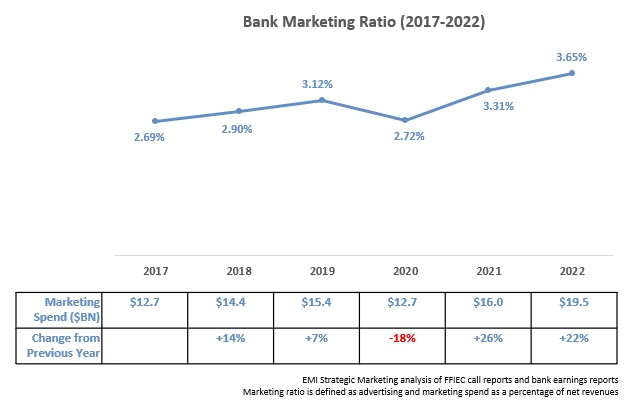
EMI Strategic Marketing performed a detailed analysis of advertising and marketing expenditures for c. 30 leading U.S. banks and found an 8% rise in spend in 2024, reaching more than $22.5 billion. Bank marketing spend was initially negatively impacted by COVID – falling 18% in 2020 – then it rebounded strongly by 26% in 2021 and 22% in 2022. The rate of growth has averaged 8% over the past two years, in line with a 9% CAGR since 2017.
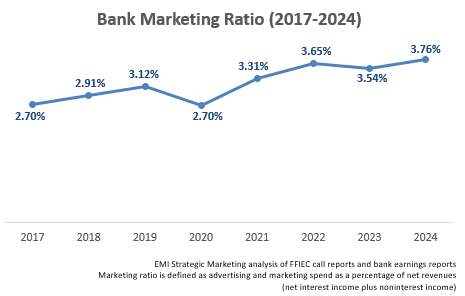
The bank marketing ratio (advertising and marketing spend as a percentage of net revenues) rose by 22 basis points to 3.76% in 2024. This ratio has grown well above pre-pandemic levels.
- Traditional banks are investing to build their brands to support expansion into new geographic markets and new financial categories and to counter the growing threat from fintechs
- Digital challengers like SoFi and LendingClub have made significant investments in marketing to build brand awareness
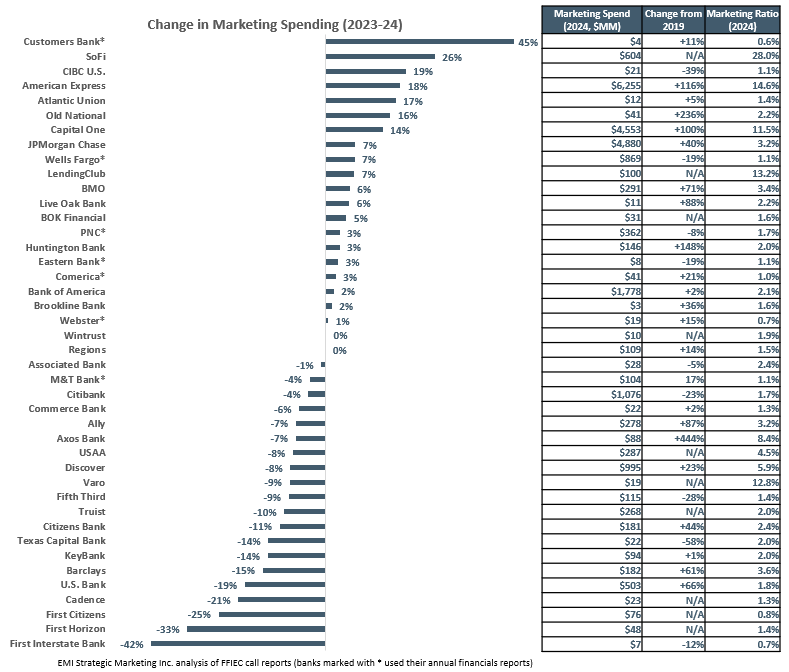
The overall rise in marketing spending was driven by leading financial advertisers like American Express (up 18% to $6.3 billion) and Capital One (up 14% to $4.6 billion). Both banks invested more than 10% of their net revenues on marketing. They were among the five banks – including JPMorgan Chase (up 7% to $4.9 billion), Bank of America (up 2% to $1.8 billion) and Citi (down 4% to $1.1 billion) – that spent more than $1 billion in marketing in 2024.
Although Citi was one of several banks that reduced their marketing budgets in 2024, it is important to apply a longer lens to some of the banks. For example, U.S. Bank reduced its advertising and marketing spend from $623 million in 2023 to $503 million in 2024. However, since its annual spend was less than $400 million between 2018 and 2022, its 2024 spend represents its continued strong commitment to marketing investment. The chart below shows the change in advertising and marketing by banks between 2023 and 2024 and also includes marketing ratios as well as change in spend from the years 2019 (pre-COVID) to 2024. (The extent and timing of advertising campaigns can also impact overall spend levels from year to year.)
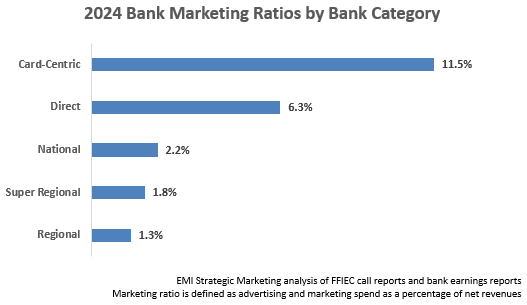
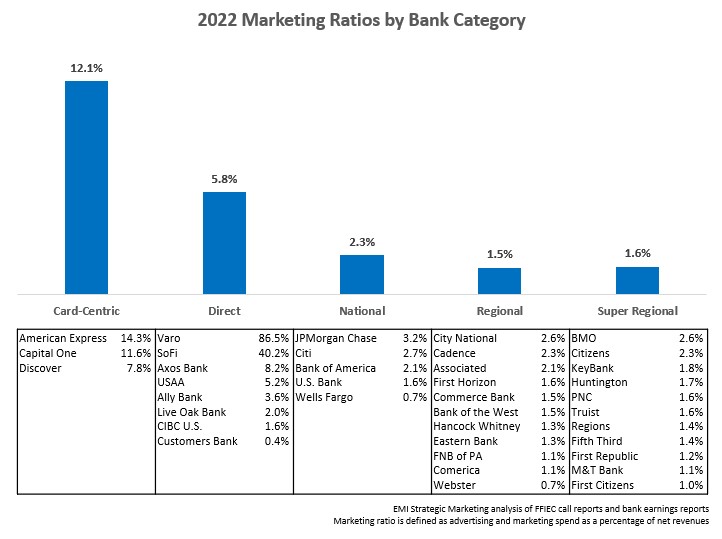
There is a significant difference in marketing ratios between different bank categories:
- Card-Centric banks (e.g., American Express, Capital One, Discover) have high marketing ratios as they aggressively market credit cards (and in many cases personal loans) nationally.
- Direct banks/fintechs (e.g., SoFi, Ally, Varo) need to build brand awareness in order to market their financial solutions nationally, and do not have the benefits – and the costs – of a branch network.
- National banks like JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America look to build their brand across the U.S., while also devoting marketing to support their branch presence.
- Super regional and regional banks concentrate more of their marketing resources within their footprints.
For 2025, we expect that bank marketing spending will continue to rise, based on:
- Strong macroeconomic conditions
- Increased consumer and business confidence
- Digital challengers building their brands to raise awareness and win share from traditional banks
- Traditional banks investing in established and emerging marketing channels to thwart competitive inroads from digital challengers, support expansion into new markets, and make up for the scaling back of branch networks in existing markets