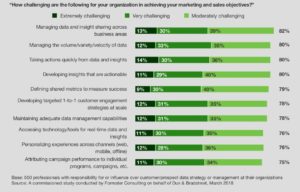
A recent Forrester/Dun and Bradstreet survey revealed that only about half of sales and marketing decisions at B2B companies with over 500 employees are made based on data. The following summary from MarketingProfs shows that challenges to the effective use of data abound: From gathering to application to measurement, all are seen as either “extremely” or “very” challenging by a large portion of the respondents.
The paradox here is that businesses are awash in data today. Companies are spending vast amounts on software, hardware, and services related to data acquisition, management, and display. Moreover, businesses are constantly talking about data and the need to make better use of it. Unfortunately, neither these solutions nor the organizational desire solves the problem. In fact, the solutions often make the problem worse because they are seen (and sold) as a silver bullet and enable managers to check a box saying they are pursuing a “data initiative.”
The reality is that the problem lies not in a lack of will or technology. It lies in a lack of focus—a lack of strategy around data management and analytics. When you can measure anything, you do…but more measures mean more data and more difficulty making it all align. More data also mean more potential interpretations—and a decreased likelihood of consensus around what the data mean and the implications.
To construct an effective data and analytics strategy, marketers need to answer the five questions below. You’ll see that several are much more about strategy than data. Why? Because to capture and leverage the right data, we must first be clear on strategy.
- What are the key stages of the customer journey? The point of marketing and sales is to influence behavior towards revenue generation. If you don’t know the path customers will follow that will generate revenue, what good is your data?
- What activities are we undertaking today to move people through those stages? Marketing and sales should be targeting points on the customer journey with activities designed to influence behavior. Organizing activities along the journey ensures that you will use data about those activities and customers in the right way.
- What should be the measure(s) of success for the impact these activities are having? Once you have aligned activities with the journey, identify ways of assessing whether those activities are successful, specifically with respect to the goal of moving from one stage to the next.
- How can we align data we have or could plausibly get with these measures? Effectively using data to make decisions depends on being able to capture the right data consistently and with confidence. If it’s hard to acquire data or the data is subject to skepticism in the organization, it will never be used.
- What decisions will we make based on the data? Imagine if, for a given measure or data point, one month it’s high and the next month it’s low. What decision will that trigger? If you can’t articulate the decision that will flow from the data, why capture the data in the first place?
To be clear, answering these questions is NOT easy for most companies. Data strategy isn’t easy. It’s actually much harder than buying software or hiring consultants to deliver more data and more measures through more systems. But without that hard work to decide what data and what measurements can really impact business outcomes, it’s unlikely that surveys like the one above will show any better results.