The largest U.S. banks have been publishing their quarterly and full-year financials over the past two weeks. Within these reports, we can discern a number of channel-related trends. These trends have a direct impact on how banks interact with their customer base in terms of providing everyday banking and value-added services as well as cross-selling additional products and services.
We’ve listed these key channel trends below:
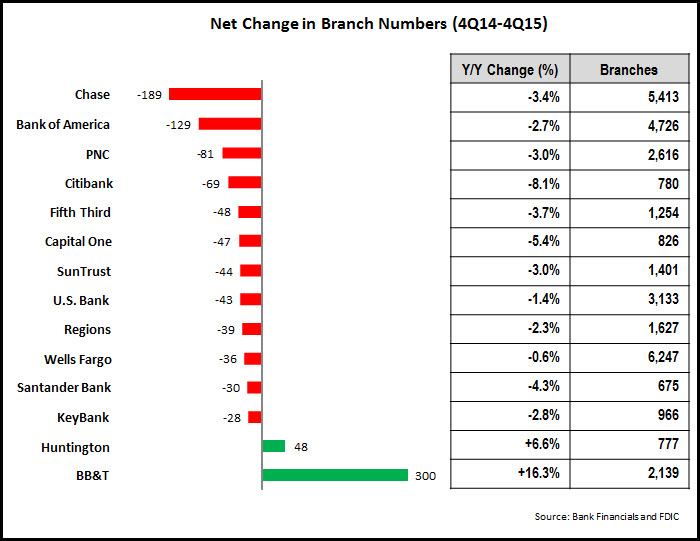
- Banks are continuing to reduce their branch networks. According to SNL Financial, the total U.S. branch network fell by 1,614 branches and is now at 92,997, a decline of 1.7%. These declines are driven by banks’ desire to cut costs, as well as from a recognition that greater usage of self-service channels for everyday banking transactions may enable banks to reduce bank density. The following chart looks at net changes in branch numbers for leading banks with more than 500 branches:
Citibank reported that it plans to close an additional 50 branches in the first quarter of 2016 as it exits certain markets (including Boston) and will concentrate its branch presence in six key metro markets. It is worth noting that in other markets where Citibank has cut its branch presence, it claims to have retained over 50% of deposits through its online and mobile channels.
- Banks are overhauling branch design and staffing. Not only are banks reducing their overall branch numbers, they are changing how branches are designed and staffed. In its 4Q15 earnings conference call, SunTrust mentioned that it is relocating to new, smaller branch locations in Richmond and Raleigh, which will reduce its square footage in these markets by half. Overall, it has reduced its branch footprint by 2.5 million square feet over the past four years. PNC reported that 375 of its 2,600 branches have been converted to its Universal Banker model, and it plans to convert an additional 100 branches in 2016.
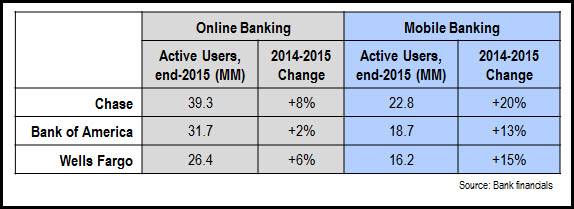
- Mobile banking is maintaining its strong growth trajectory. According to Javelin Strategy & Research, 30% of U.S. adults used a mobile banking service weekly in 2015. Reflecting this trend, leading banks continue to show double-digit y/y growth in mobile banking users (Chase +20% to 22.8 million; Bank of America +13% to 18.7 million; and Wells Fargo +15% to 16.2 million). These customers are also using mobile banking for a greater variety of transactions. For example, Bank of America reported that mobile banking’s share of total deposit transactions rose steadily from 4% in 4Q12 to 15% in 4Q15.
- Online banking usage remains strong…and is growing. While mobile banking garners most of the headline in financial trade press, online banking remains a key customer service channel, and some leading banks continue to register strong growth rates in online banking users. This is likely due to a number of factors, including overall account growth, increased customer comfort with using online banking, new online banking functionality, as well as lingering concerns over mobile banking security. The following table compares 2015 online and mobile banking users and growth rates for Chase, Bank of America and Wells Fargo:
We expect that as banks continue their migration towards self-service channels for a growing number of everyday banking transactions, banks will continue to scale back their branch networks. This will involve reducing branch density in particular markets, as well as exiting markets where they lack a critical mass or where their branches are underperforming. However, banks in general want to maintain a physical presence in markets, so they can leverage the power of the branch as both a sales channel and a branding beacon.
In addition, banks need to provide a consistent user experience across their online and mobile channels. In the short term, banks will continue to provide more functionality in the online channel, as consumers build trust in using their mobile devices for more complex financial transactions. But the distinctions between online and mobile channels are blurring, and banks are already starting to refer to “digital channels” to encompass desktop, tablet and mobile channels. Even the traditional delineations between “online” and “offline” channels are breaking down, as banks showcase their digital services in branches, and as digital channels include functions to enable customers make in-branch appointments.