A recent American Banker article discussed a credit card rebound, referring to data from the Federal Reserve that showed strong growth in revolving consumer credit in April 2014. This supports findings in a recent EMI blog (“Four Takeaways from Credit Card Issuer 1Q14 Financials“), which found signs of an improvement in credit card outstandings for the leading issuers.
The FDIC has recently published bank data for the first quarter of 2014. EMI’s analysis of this data provides further evidence that the decline in credit card outstandings is bottoming out.
- Credit card outstandings fell 0.3% between end-1Q13 to end-1Q14. This marked an improvement from a decline of 0.7% between end-2012 and end-2013.
- The overall decline is due to the outstandings performance of the four largest issuers (Chase, Bank of America, Citi, and Capital One) who together accounted for 63% of total industry outstandings at the end of March 2014. These four leaders reported a 2% y/y decline in outstandings.
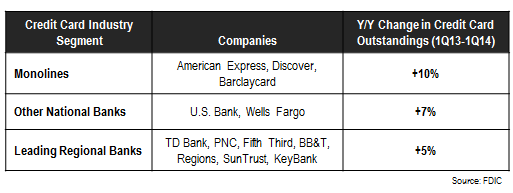
- Outside of these four issuers, outstandings for the rest of the industry rose 3% y/y. Growth in outstandings is led by a number of sectors, as summarized in the following table:
Furthermore, even though the leading issuers have been dragging down overall outstandings performance for a number of years, there are indications that these declines are bottoming out, and loan portfolios are even poised to grow in the coming quarters:
- Chase credit card outstandings were virtually unchanged between end-1Q13 and end-1Q14. At its 2014 Investor Day, Chase reported growth in its core card loan portfolio (excluding its run-off portfolio), although its focus has been on growing volume rather than loans
- Bank of America reported a 1% decline in card outstandings, but expects this decline in bottom out this year. Card issuance is strong at more than 1 million new accounts in 1Q14 (compared to a quarterly average of about just over 800,000 in 2012)
- Capital One reported that its domestic card loan portfolio fell 3% y/y in 1Q14, mainly due to its run-off portfolio. However, it reported that it was seeing loan growth in some key consumer segments, such as transactors. And in a recent Morgan Stanley conference, Capital One claimed that it expects loan growth in July, earlier than anticipated.
So, how can issuers best prepare for outstandings growth? The following are three quick tips:
- Set realistic expectations. Don’t expect a return to the outstandings levels that prevailed prior to the 2008 financial crisis and resulting recession. Consumer attitudes to credit card have changed since then, as they see credit cards less as an easy source of credit (evidenced by high monthly payment rates) and more as an effective payment tool (seen in the continued strong volume growth rates)
- Prepare the groundwork for future growth. Rather than driving up loan growth (and potential charge-off rates) through overly aggressive pricing offers, issuers should concentrate on the basics: providing a robust product suite with value-added features to meet cardholder spending and borrowing needs; building flexible reward programs; and setting pricing based on appropriate levels of risk and reward.
- Focus efforts on existing customers. Traditionally, credit card issuers have focused their marketing on new customer acquisition. Now, a new generation of credit card issuers (led by Wells Fargo and followed by regionals banks that have recently started to issue cards in-house) are growing their portfolios by cross-selling credit cards to existing bank clients. In addition, simple card acquisition is not enough; issuers need to develop communications and offers to drive activation, retention, preference and increased usage, thereby optimizing customer lifetime value.