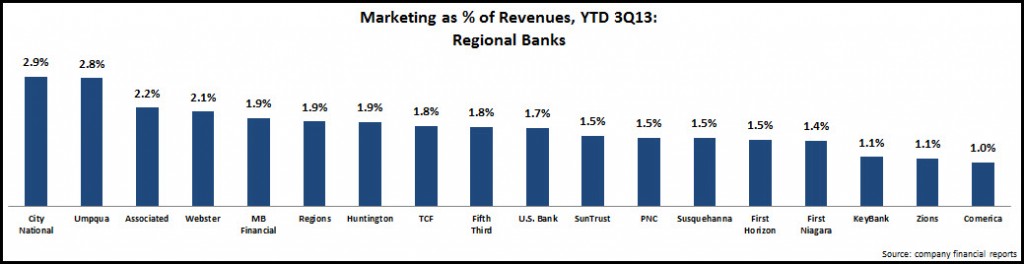
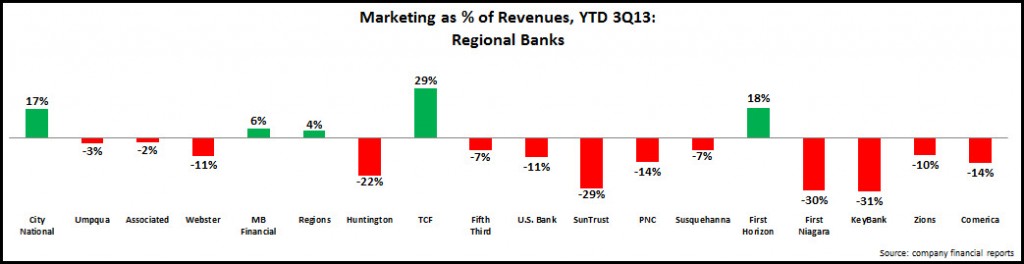
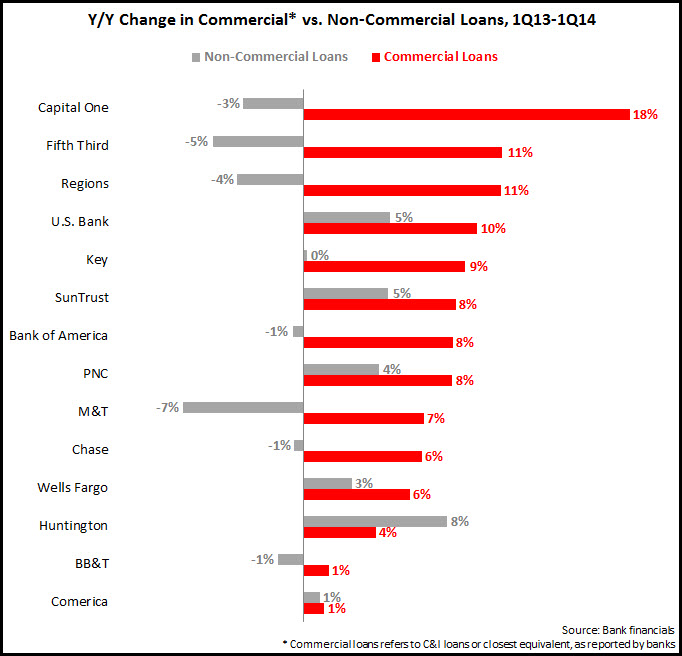
EMI analysis of 14 leading U.S. banks found 7.4% y/y growth in commercial and industrial (C&I) loans in the first quarter of 2014, down from a 7.9% y/y growth rate in 4Q13. Though three banks (Capital One, Fifth Third and Regions) reported double-digit loan growth, only Capital One exceeded the 4Q13 y/y growth rate. Six of the 14 banks—including two of the top three commercial lenders: Wells Fargo and Chase—had lower y/y growth in 1Q14 vs. 4Q13.
In addition, as banks compete aggressively for commercial loans in the current low interest rate environment, yields continue to decline. Of the 13 banks providing C&I loan yield data, all reported double-digit y/y basis point declines. Banks with the largest y/y declines included Fifth Third (-55 bps to 3.35%) and KeyBank (down 49 bps to 3.29%). For nine of the 13 banks, yields are now below 3.5%.
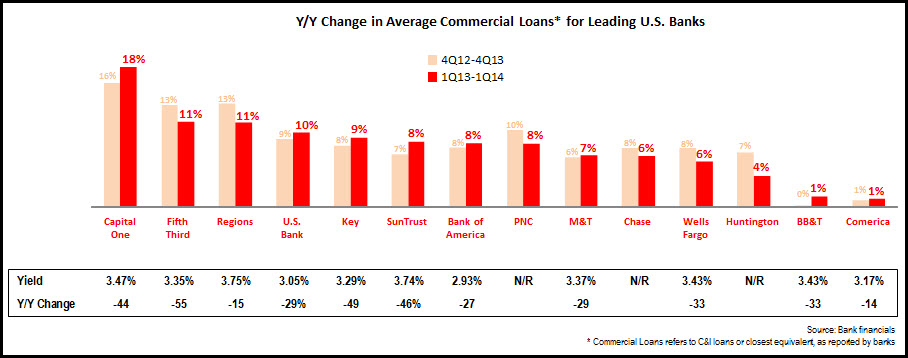 In spite of the slight decline in C&I loan growth rates, this loan category continues to propel overall bank loan growth. While the 14 banks generated total y/y loan growth of 2% in 1Q14, their non-commercial loan growth was just 0.4%.
In spite of the slight decline in C&I loan growth rates, this loan category continues to propel overall bank loan growth. While the 14 banks generated total y/y loan growth of 2% in 1Q14, their non-commercial loan growth was just 0.4%.
 The following are four quick tips for banks to maintain—and even accelerate—commercial loan growth:
The following are four quick tips for banks to maintain—and even accelerate—commercial loan growth:
- Target specific geographic markets or vertical industry segments, where the bank already has—or can quickly develop—dedicated capabilities
-
Re-commit to the small business segment by providing services and support tailored to their unique characteristics and needs
-
Develop initiatives to increase commercial loan utilization rates (which continue to trail historic averages for many banks, although many banks did highlight recent growth in utilization rates)
-
Identify and dedicate resources to capture growth in particular loan categories (such as CRE), which have been ignored in recent years in the aftermath of the financial crisis