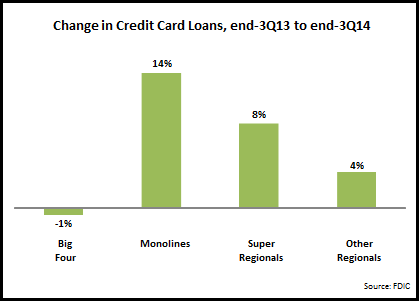
EMI analysis of the leading U.S. credit card issuers’ latest quarterly financials—as well as FDIC call reports—revealed the following trends in outstandings, volume and charge-off rates. According to the latest call report data from the FDIC, end-of-period outstandings rose 0.9% between 3Q13 and 3Q14. Three of the four issuer segments grew card loans, with the Big Four issuers continuing to act as a brake on stronger overall growth.
- End-of-period card loans for the Big Four issuers (Chase, Bank of America, Citi and Capital One, which account for 66% market share) fell 1%. Chase and Capital One reported loan growth (+3% and +4% respectively), while Citi (-6%) and Bank of America (-1%) continued to decline.
- The four main card “monolines” had the strongest loan growth, led by Barclaycard (+32%) and Synchrony (+24%). American Express and Discover each reported 7% growth.
- The super-regionals maintained their strong loan growth rate, with Wells Fargo rising 11% (maintaining its strong recent momentum) and U.S. Bank up 5%.
- Other regional bank card issuers* had steady card growth. Within this segment, SunTrust was the standout performer, up 22% y/y. Other regionals banks with relatively strong credit card loan growth included PNC (up 5% to $3.9 billion), Fifth Third (rise of 7% to $2.1 billion) and Regions (+8%, to $0.9 billion).
Bank cards issuers are ramping up efforts to cross-sell credit cards to existing banking customers.
- Wells Fargo is leading this push, with its credit card penetration of retail banking households reaching 40% in 3Q14 (up from 28% in 3Q11). To target its affluent clients, Wells Fargo recently launched American Express-branded credit cards.
- Regional banks are seeking to replicate the approach of the super-regionals; Regions reported that credit card penetration was 15% in 3Q14, up two percentage points y/y.
- Even the top issuers are looking to tap into cross-sell opportunities: Bank of America reported that 64% of new cards issued in 3Q14 were to existing bank clients.
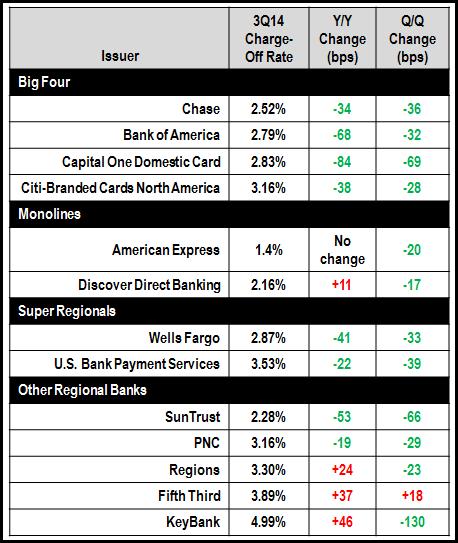
In recent years, issuers have focused much more on growing volumes rather than loans. Even as issuers are now refocusing on growing outstandings, they continue to seek to grow card volume, through tiered rewards programs and acquisition/activation offers. Issuers leading the way include Capital One (17% y/y rise in general-purpose card volume), Wells Fargo (+16%), Chase (+12%) and American Express (+9%). Credit card charge-offs rates continue to decline, with the scale and duration of the decline surprising the issuers themselves. Of the 13 issuers in the table below, seven had 3Q14 charge-off rates below 3%, and eight of the issuers reported y/y declines.
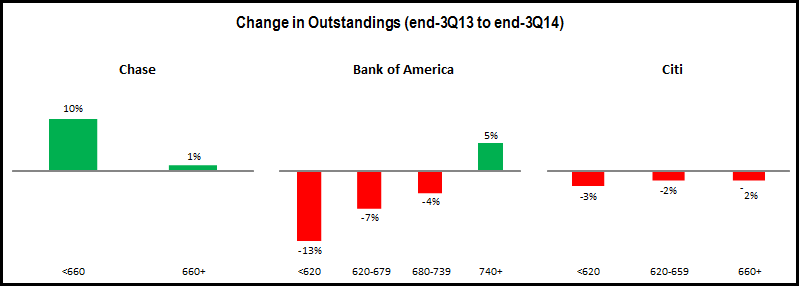
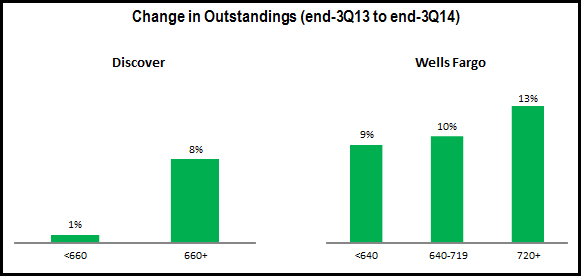
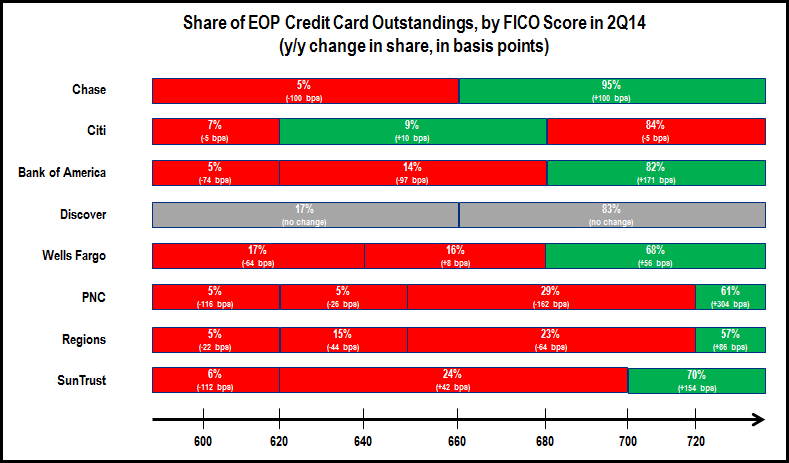
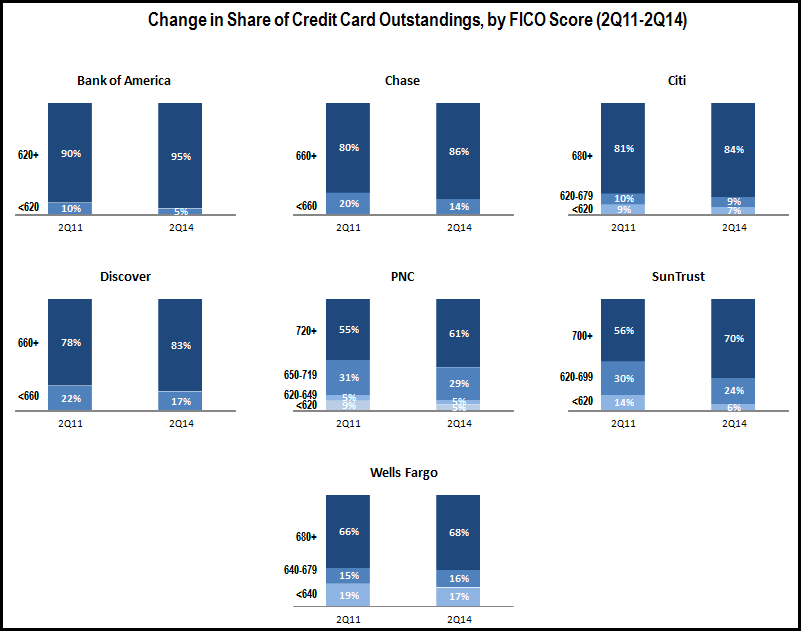
Issuers continue to focus outstandings growth on higher-FICO segments, with some exceptions.
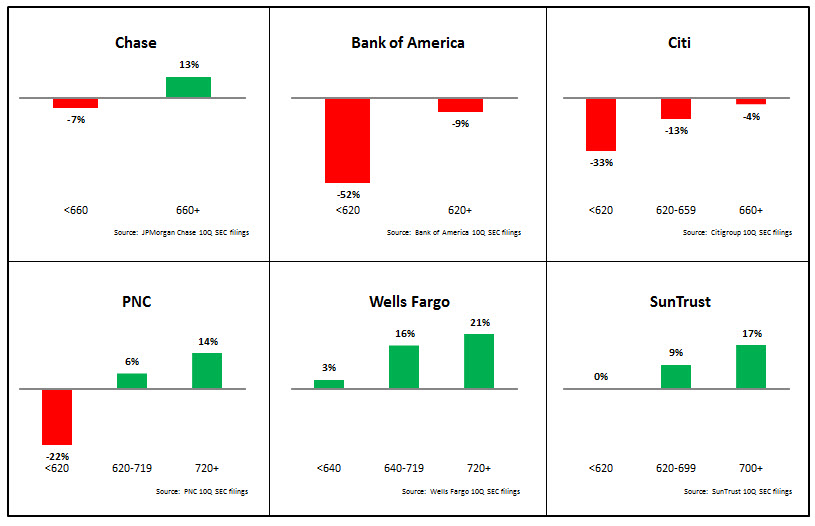
- Big Four Issuers: For Bank of America, outstandings for the 740+ FICO segment rose 5%, but outstandings fell 6% for the <740 segment. However, Chase bucked the general trend with stronger growth for the <660 FICO segment.
- Monolines and super regionals: both Discover and Wells Fargo reported strong outstandings growth between end-3Q13 and end-3Q14, with stronger growth performance for higher FICOs.
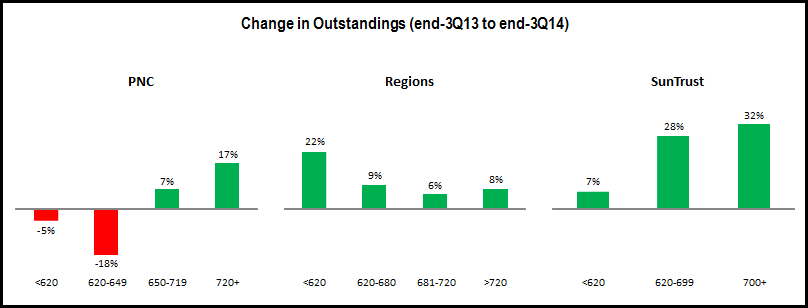
- Other regional bank card issuers: PNC and SunTrust following the general pattern, with stronger outstandings growth for higher FICOs. However, Regions’ <620 segment outstandings rose 22% (albeit from a low base).
* Other Regional issuer segment comprised of the following banks: TD Bank; PNC; Fifth Third; BB&T; Citizens Bank; Regions; SunTrust; Commerce Bank; KeyBank; and BBVA Compass.