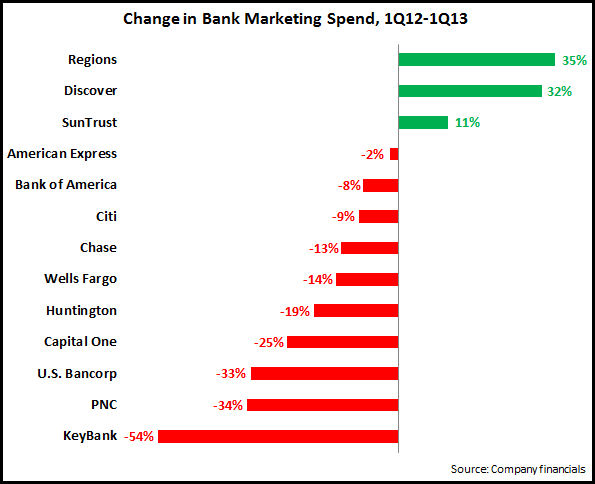
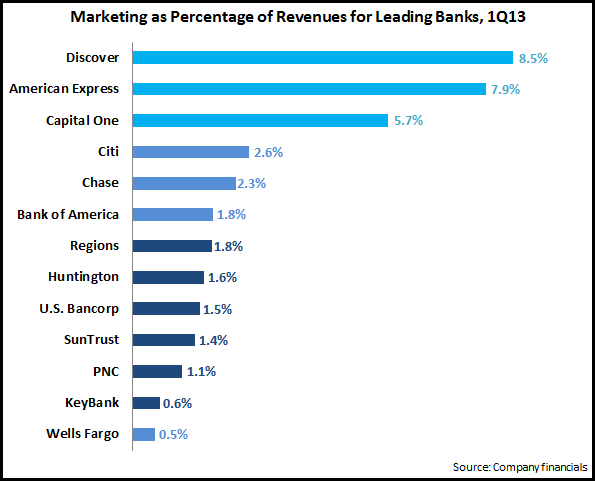
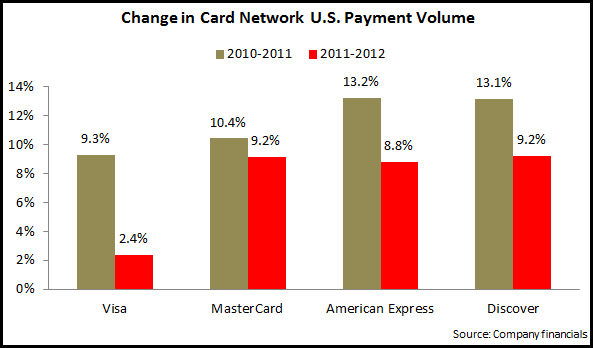
EMI analysis of the largest credit card issuer financial results for 1Q13 reveals the following trends:
- Outstandings (11 issuers reporting, analysis excludes Capital One, which acquired the HSBC card portfolio in 2012, so its growth rate would skew the data): A weighted average of 11 leading credit cards issuers shows that average credit card outstandings fell 2% year-over-year (y/y) in 1Q13. The three largest issuers – Chase, Bank of America and Citi – all reported y/y declines. However, outstandings growth came from Wells Fargo (who reported that credit card penetration of retail banking households rose from 30% in 1Q12 to 34% in 1Q13), regional banks with relatively small portfolios (e.g., PNC, SunTrust and Fifth Third), as well as “monolines” (American Express and Discover). These outstandings trends bear out the industry predictions we made in a blog at the start of 2013.
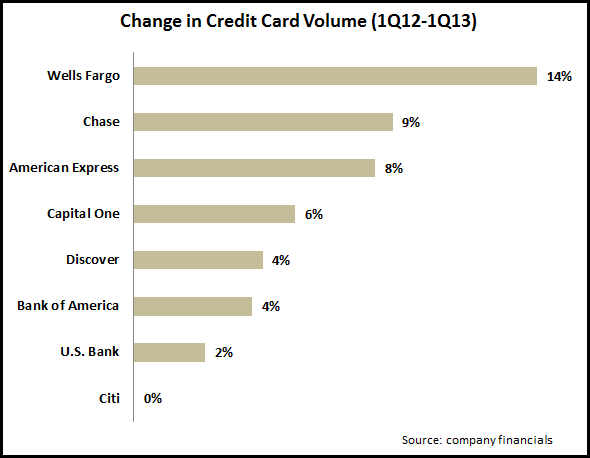
- Volumes (8 issuers reporting): leading issuers grew credit card volume 6% y/y in 1Q13, which is relatively consistent with recent quarters. However, growth rates have moderated from the 2010-2011 levels, when issuers were overwhelming focused on building volumes. Wells Fargo led the way with a 14% volume growth rate, driven by an 18% rise in new consumer credit card accounts.
- Revenues and expenses (5 issuers reporting): Revenues rose 2% y/y, led by Discover (+11%) and American Express (+5%). The lack of outstandings growth means that net interest income remains relatively anemic, with a rise of 1% y/y. Noninterest income grew 5%, with relatively healthy growth rates from American Express, Discover and Bank of America. Noninterest expenses fell 1%, with both Chase and Bank of America reporting significant declines (reductions of 8% and 7%, respectively). Provisions for loan losses rose 5%, albeit from very low levels in 1Q12.
- Charge-off rates (11 issuers reporting): The weighted average charge-off rate for these 11 issuers was 3.62%, down 65 basis points (bps) y/y, but up 5 bps q/q. 10 issuers reported charge-off rate y/y declines. The exception was Capital One, which acquired the HSBC credit card portfolio (with a higher charge-off rate) in 2012. Compared to 4Q12, 10 issuers reported charge-off rate increases and the other two were unchanged, indicating that the era of charge-off rate declines may be coming to an end.
- 30+ day delinquency rates (8 issuers reporting): 7 of the 8 issuers providing 30+ day delinquency rate data reported y/y declines. As with the charge-off rate, the exception is Capital One. Interestingly, 7 of the 8 issuers reported q/q declines. The exception was American Express, whose 30+ day delinquency rate was unchanged. So, while the period of charge-off rate declines may be ending, the continued decline in delinquency rates will moderate charge-off rate increases.