The emergence of virtual channels, the need to cut costs and speculation of more industry consolidation are all spurring banks to reconsider their branch networks. Recently, EMI Strategic Marketing Inc. published blogs on the changing role of the branch, as well as trends in branch numbers for leading U.S. banks.
Banks have reiterated their commitment to the branch channel, but many are unlikely to maintain branch numbers at current levels. Bank decisions of branch numbers and deployments are increasingly based on an analysis to the bank’s relative strengths in different markets. Is the bank’s branch network spread too thinly, with few branches and low deposit shares in many markets? Does it have critical mass in terms of branch numbers and/or deposit share in particular market? If it does not have sufficient scale at present, should it expand its branch network organically or through acquisition? Or should it leave some markets?
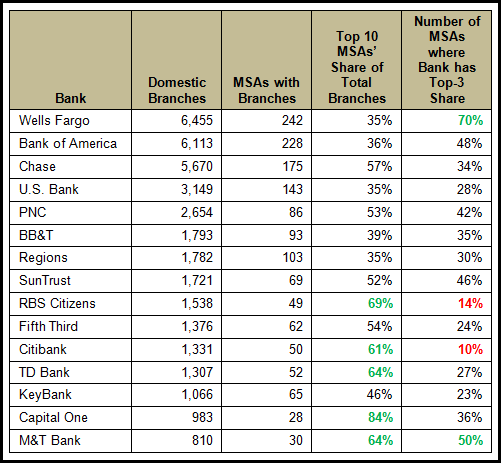
EMI Strategic Marketing Inc. analyzed end-2Q11 FDIC data on the branch footprint of the top 15 retail banks. (Note: this does not include M&A activity over the past year, such as PNC’s acquisition of RBC Bank.) We focused on the number of metropolitan statistical areas (MSAs) where these banks had branches, branch concentration levels, and market strength indicators.
- The banks with the most extensive branch networks are Bank of America and Wells Fargo, who both have branches in more than 200 MSA markets.
- Regional banks naturally have a more concentrated branch presence. RBS Citizens, PNC and M&T all have more than 60% of their branches in 10 markets.
- RBS Citizens has top-three share in only 14% of the 49 markets where it has a physical presence. Recent speculation indicates it may sell off its branch network in Illinois and Michigan. The bank has branches in seven MSAs in these two states, but does not have a top-three deposit share in any of these markets.
- Market strength: Wells Fargo has a top-three deposit share in 70% of its MSAs. Four other banks (M&T, Bank of America, SunTrust and PNC) are ranked in the top three in more than 40% of their markets.
- In late 2010, Citigroup announced that it would be concentrating on 16 U.S. metro markets. This helps to explain why 61% of Citibank’s branches are in just 10 MSAs. On the other hand, it has five or fewer branches in more than half of its markets. Given its stated objective to concentrate its efforts on about 15 metro markets, we can expect Citibank to leave many of these markets where it has a token presence. However, it will be aiming to significantly grow share in its target markets.
- Capital One, which has built a retail branch presence in recent years through acquisition, has 84% of its branches in just 10 MSAs. (In fact, 57% of Capital One branches are in just two MSAs: Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV and New York-Northern New Jersey-Long Island, NY-NJ-PA.)