EMI analyzed bank marketing data of 25 leading U.S. banks and found a 4% y/y decline in marketing expenditure for the first nine months of 2013. During this period, marketing spending accounted for 2.6% of net revenues.
Our analysis finds that marketing expenditure levels and changes vary significantly by bank type .
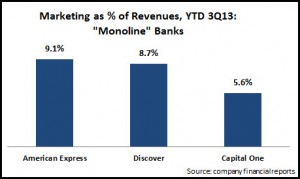
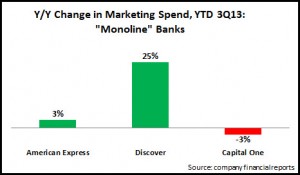
- Monolines: These banks are characterized as having a strong dependence on their credit card operations. The three banks in this segment—American Express, Discover Financial and Capital One—allocated 7.8% of their revenues to marketing in the first 9 months of 2013. Capital One’s spend levels are relatively lower, as it has transitioned over the past decade to be more like a full-service bank, with a network of 900+ branches. The ‘monoline’ segment is also bucking the overall trend, with a 4% y/y rise in marketing spend.
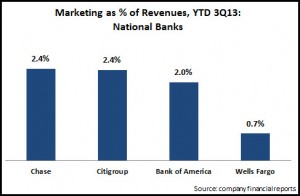
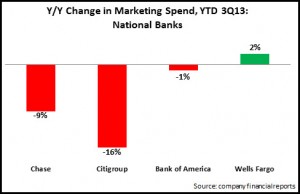
- National banks: These megabanks invest about 2% of revenues in marketing to promote their brands, support their extensive physical and virtual channels, and advertise their wide array of financial products and services. As these banks (which include JPMorgan Chase, Wells Fargo, Citigroup and Bank of America) are under pressure to maintain profitability in a low/no growth environment, they reduced marketing spend 8% y/y. Wells Fargo stands out, insofar as its marketing spend as a percentage of revenues is much lower than its peers, as it has traditionally focused its revenue-generating activities on its branch network. However, Wells Fargo was the only one of these four national banks to report y/y marketing growth for the first three quarters of 2013.
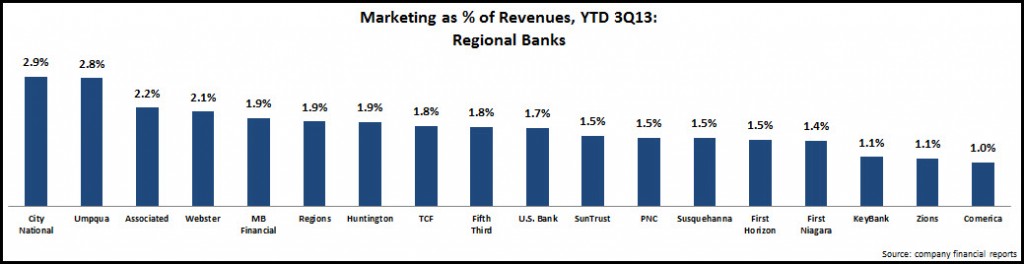
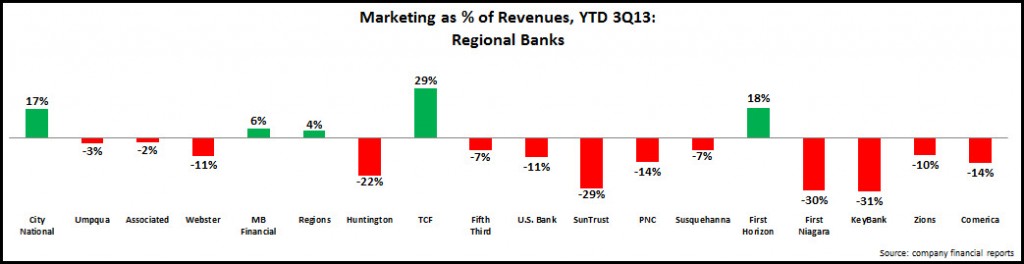
- Regional banks: The 18 regional banks analyzed by EMI allocated 1.6% of their revenues to marketing over the first 9 months of 2013. Under pressure to cut costs and maintain profitability in the absence of revenue growth, these regional banks cut marketing budgets by 13%, led by large regionals like KeyBank (-31%) and SunTrust (-29%).
The extent to which banks ramp their marketing spend will be based on whether they see significant revenue growth opportunities, which in turn is dependent on economic growth. And there are some positive signs in this regard, with the OECD projecting that U.S. GDP growth will rise from 1.7% in 2013 to 2.9% in 2014 and 3.4% in 2015.