The following are four key takeaways from the 1Q14 financials for 13 U.S. banks with significant credit card operations.
- Some improvement in outstandings performance
- Continued volume growth
- Charge-off rates at or below historic norms
- Little change in industry profitability
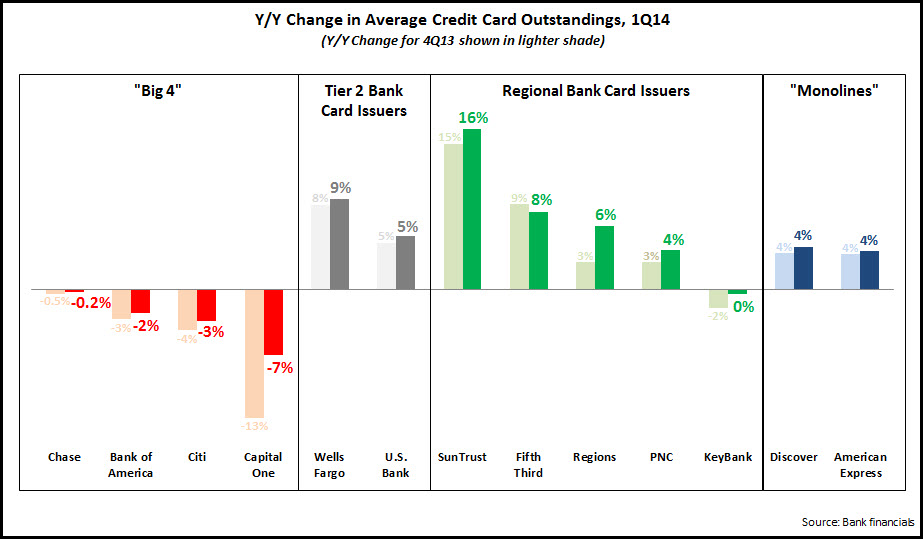
Average outstandings for the 13 issuers in 1Q14 were unchanged y/y, an improvement from a 2% y/y decline in 4Q13.
- For the four largest issuers—Chase, Bank of America, Citi and Capital One—the rate of decline in average outstandings improved from 5% in 4Q13 to 3% in 1Q14. Capital One highlighted progress made in working through run-off portions of the acquired HSBC portfolio, and it expects outstandings growth in the second half of 2014. Other issuers are ramping up new account production: Bank of America originated more than 1 million new accounts for the third consecutive quarter, while Chase opened 2.1 million new accounts in 1Q14, 24% higher than 1Q13.
- For Tier 2 bank card issuers—Wells Fargo and U.S. Bank—the rate of outstandings growth rose from 7% in 4Q13 to 8% in 1Q14. Wells Fargo benefitted from the continued growth in credit card penetration of its retail banking households, which rose from 34% in 1Q13 to 38% in 1Q14.
- Similarly, regional bank card issuers grew average loans 6% in 1Q14, compared to 5% in 4Q13.
- Credit card loan growth rates for the former ‘monolines’—American Express and Discover—were unchanged at 4%.
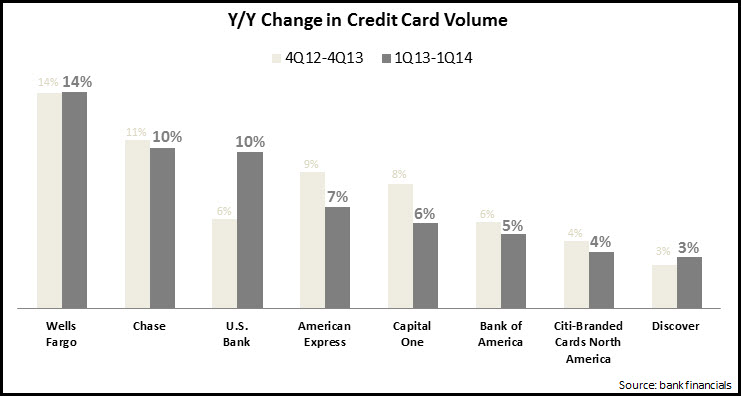
Eight leading issuers reported 7% y/y growth in credit card volume in 1Q14, slightly lower than the 4Q13 increase. Three issuers—Wells Fargo, Chase and U.S. Bank—reported double-digit percentage growth in 1Q14. In general, issuers appear committed to continuing to push volume growth, as evidenced by the launch of new rewards cards with strong earnings potential (e.g., American Express Everyday), as well as enhancements to existing rewards programs.
12 of the 13 issuers reported y/y declines in net charge-off rates in 1Q14.
-
12 issuers now have charge-off rates below 4%. The only major issuer with a charge-off rate above 4% is Capital One, who reported that the acquired HSBC card portfolio added about 25 basis points to its charge-off rate in 1Q14. It expects that the impact of this portfolio would be mostly gone by the end of the second quarter.
-
10 reported charge-off rate increases between 4Q13 and 1Q14. This were attributed to seasonality, as well as indications that rates are starting to move back towards normalized levels as issuers seek to build outstandings growth.
-
However, it is worth noting that delinquency rates—which have traditionally been a leading indicator of future directions in charge-off rates—continue to decline on both a y/y and q/q basis for most issuers.
The six issuers who provide card-related revenue and cost information, reported that card profitability was virtually unchanged between 1Q13 and 1Q14. Revenue growth remains elusive, declining 1%, as net interest income fell 2%. The relatively strong rise in card volume did not translate into similar growth in noninterest income, as issuers are enhancing their rewards programs, which eats into interchange income (e.g., Discover reported that its rewards rate 11 bps y/y to 1.03% in 1Q14). Noninterest expenses (reported by five issuers) were unchanged y/y, while provisions for loan losses rose 6%, as issuers anticipate future charge-off increases.