This week, the FDIC published end-4Q12 data for all U.S. banks showing that U.S. banks’ commercial and industrial (C&I) loan portfolios rose 12% in the year to end-4Q12. This marks the sixth consecutive quarter with double-digit y/y growth, although the rate of increase has fallen from a high of 16% in 2Q12.
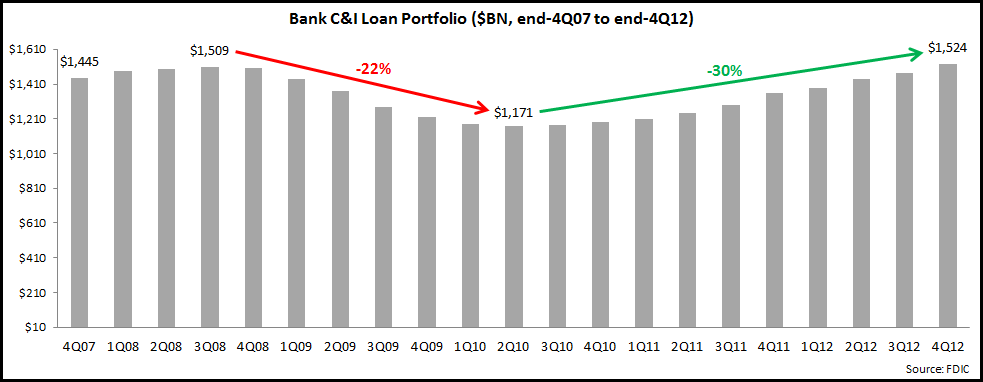
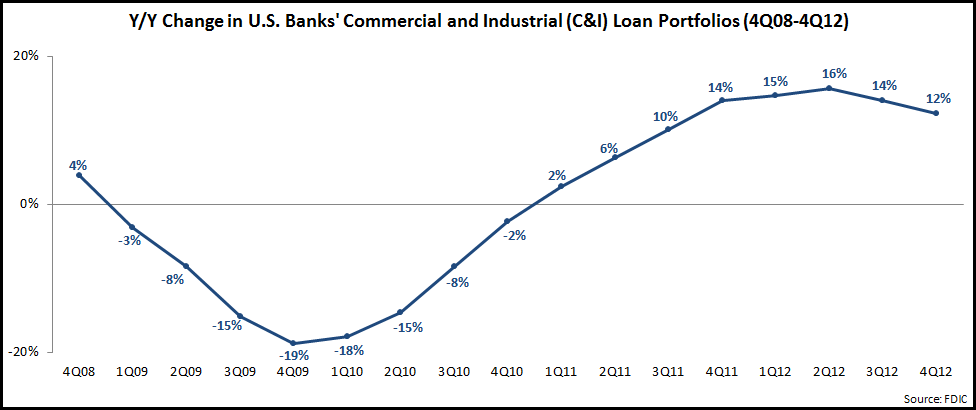 Banks are increasingly looking to commercial lending as a way to grow their overall business, but they are concerned that the current growth rate can be sustained, in particular given the precarious nature of the U.S. economic recovery. The following chart shows that the strong growth rates over the past two years has resulted in C&I loan portfolios returning to levels seen just prior to the financial crisis.
Banks are increasingly looking to commercial lending as a way to grow their overall business, but they are concerned that the current growth rate can be sustained, in particular given the precarious nature of the U.S. economic recovery. The following chart shows that the strong growth rates over the past two years has resulted in C&I loan portfolios returning to levels seen just prior to the financial crisis.
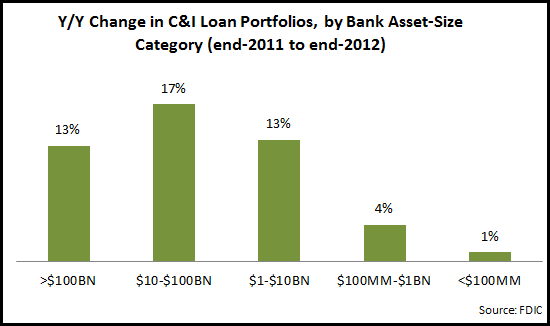
 The data also shows a market difference in C&I loan portfolio growth performance by different bank-asset classes, with larger banks significantly outperforming those with less than $1 billion in assets.
The data also shows a market difference in C&I loan portfolio growth performance by different bank-asset classes, with larger banks significantly outperforming those with less than $1 billion in assets.
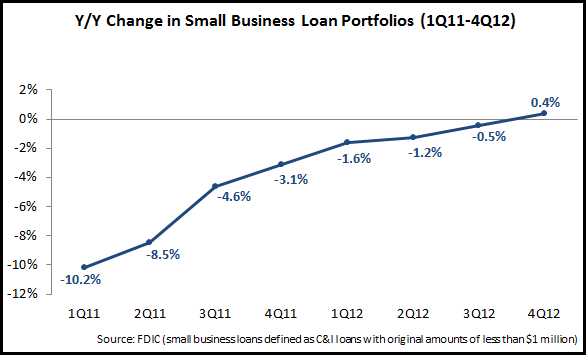
Although banks’ C&I loan portfolios have recovered strongly in recent years following the financial crisis, small business loan portfolio growth remains elusive. The FDIC started to report small business loan data in 1Q10, and since then small business loan portfolios have decreased by 10%. However, there are signs that this period of decline has finally bottomed out, with a y/y increase of 0.4% at the end of 2012.
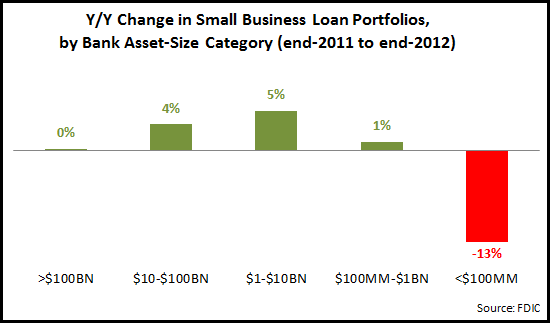
As with their overall C&I loan portfolios, larger banks–led by banks with $1-$10 billion in assets–reported strongest small business loan portfolio growth, while community banks with less than $100 million in assets saw a 13% y/y decline in their small business loan portfolios.