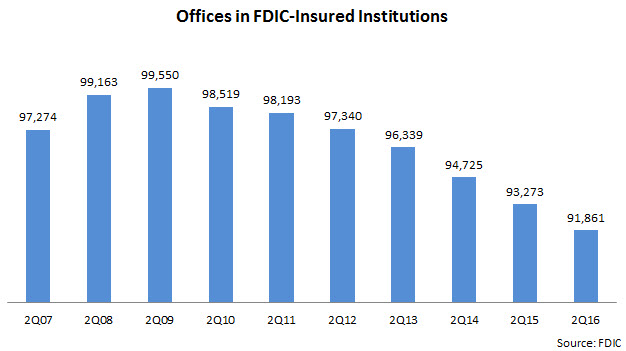
According to the FDIC, U.S. banks have been cutting branches steadily in recent years. Offices in FDIC-insured institutions reached a high of 99,500 at the end of 2Q09, but have declined by almost 8% since then, to less than 92,000.
Bank branch reductions are primarily driven by two factors: cutting costs in a low-revenue-growth environment; and the belief that customers’ increase use of electronic channels for everyday banking needs means that banks need fewer branches. According to the American Bankers Association, 73% of U.S. adults identified the Internet and mobile as their preferred banking methods, with only 14% naming branches. However, customers remain committed to branches. According to a March 2016 Accenture survey, 87% of North American banking customers expect to still use bank branches two years in the future. A branch strategy that simply consists of branch cuts fails to take into account customers’ ongoing branch affinity, as well as ignores the significant role that branches can play in helping banks meet sales and service goals. Here are four strategies that banks can follow to optimize their branch investments:
- Create specialist branches. Some banks are opening offices to target specific segments, such as commercial clients or high-net-worth individuals. For example, BMO Harris opened a commercial banking office in Dallas in June 2016, while Wells Fargo opened a Middle Market Banking office in Albany in August 2016. These branches are located, designed and staffed to cater to the characteristics and unique financial needs of these segments. Unlike traditional branches that tend to form part of a network, these specialists branches can operate on a standalone basis, thereby ensuring that costs stay under control.
- Use branches to promote digital services. Recognizing the transition to electronic channels for everyday banking transactions, banks can leverage their branch network to demonstrate the ease-of-use and value of these digital services to customers who are slow to embrace technology, while also showcasing innovations to early adopters of new technologies. Bank of America has deployed 3,800 ‘digital ambassadors’ in its branches who help customers understand and use its online and mobile banking services.
- Overhaul branch staffing. Smaller branches require fewer personnel, but the staff must be comfortable with performing a range of service and sales activities. Embracing this model, PNC plans that half of its branches will have converted to ‘universal branches’ by 2020 (18% have done so to date)
- Scale down the overall branch footprint. As they seek to reduce branch costs, banks need to take into account the benefits of having a physical presence in markets. This can involve using smaller branch formats (one extreme example is PNC’s portable 160-foot “Tiny Branch” on the West Virginia University’s Morganstown campus), reducing branch density, replacing a series of existing branches with one big flagship store, or even opening new branches in high-growth/high-potential markets. Decisions on the number, location and format of branches should be based on analyzing a number of key factors, including: competitive intensity; market size, growth and composition; current branch usage; short-term costs; and longer-term savings.