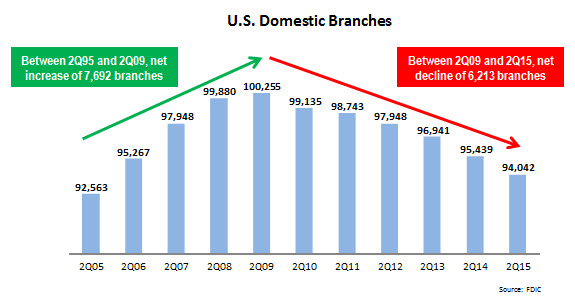
According to the FDIC, there were just over 94,000 domestic bank branches at the end of June 2015: a net reduction of almost 1,400 branches from end-June 2014, and a decline of more than 6,000 branches since the U.S. passed the 100,000 branch threshold in mid-2009.
The recent decrease in the number of branches is being driven by a number of factors, including banks’ focus on cutting costs in recent years. In addition, the emergence and strong growth of online and mobile banking usage has led to consumers significantly reducing their use of branches for transaction processing. So how are banks adapting their branch networks to this changing channel environment? An analysis of presentations by leading U.S. banks at the recent Barclays Global Financial Services Conference identified a number of ways that banks are restructuring, repositioning, redesigning and restaffing their branches to ensure that this channel survives and thrives into the future.
- Continuing to pursue branch consolidation. While banks continue to emphasize their commitment to the branch channel in general, they have cut their overall number of branches in recent years, and will continue to do so. At the Barclays conference, KeyBank reported that it had cut its branch network by 10% in the past three years, and envisages a further ongoing reduction at a rate of 2-3% per year.
- Selling off (and acquiring) branch networks. Most leading banks believe they need to have critical mass in particular markets. If they feel that they cannot achieve this goal, they may decide to exit the market entirely. Citi is exiting a number of markets, as it seeks to focus on just 6 major metro markets. Fifth Third recently announced that it is ending its branch presence in Pennsylvania. These branch sell-offs create opportunities for other banks who want to grow their presence in those markets (BB&T acquired Citi’s branch network in Texas, and F.N.B is buying Fifth Third’s 17 branches in Pittsburgh).
- Developing a hub-and-spoke approach. Rather than having a dense network of similarly-sized branches, some banks are looking to establish a hub-and-spoke approach in specific markets. This approach typically features a flagship branch as well as a reduced number of small branches. At the Barclays conference, Synovus claimed that it was applying a hub-and-spoke system. Other banks with flagship branches include Bank of America and Citibank, which now has flagship branches in four of its six target U.S. metro markets.
- Redesigning and re-staffing branches. As the branch channel’s primary role shifts from transaction processing to sales and service, leading banks are overhauling store layouts and are replacing tellers with product experts. In addition to closing or consolidating 400 branches in recent years, PNC reported that it has converted 300 branches to its universal banking model (featuring concierge stations and reformatted teller stations). In addition to providing enhanced sales and services to branch visitors, PNC claims that these branches cost 45% less than traditional branches. In terms of staffing, Bank of America reported that it has added nearly 1,200 financial solutions advisers and small business bankers over the past two years.
- Growing in-store branch networks. Banks like Huntington and U.S. Bank have significant in-store or on-campus branch networks, and remain committed to this channel. Huntington Bank recently announced that it was adding 43 in-store branches in Michigan via its relationship with Meijer Stores.
- Incorporating new functionality into online and mobile banking services to drive branch traffic. Bank of America reported that its clients used the bank’s online and mobile apps to schedule an average of 14,000 branch appointments per week in August 2015. And in September 2015, Bank of America announced online and mobile banking enhancements, which included enabling clients to make same-day financial center appointments.
- Applying guerrilla marketing tactics. Banks are becoming more creative in how they establish a physical presence to better interact with clients and prospects. Leveraging its relationship with the Green Bay Packers, Associated Bank has set up a virtual branch in the parking lot of Lambeau Field to target tailgaters.
While the overall number of branches is likely to continue to decline, most banks appreciate the key role that branches play in sales, service and branding, and remain committed to the channel. However, banks will continue to adjust branch density, design, layout, staffing and integration with other channels, in order to control costs and adapt to new consumer preferences and behaviors in how they interact with their banks.