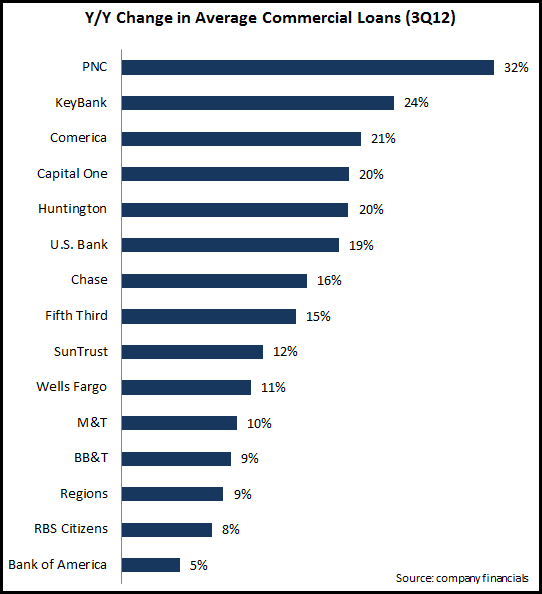
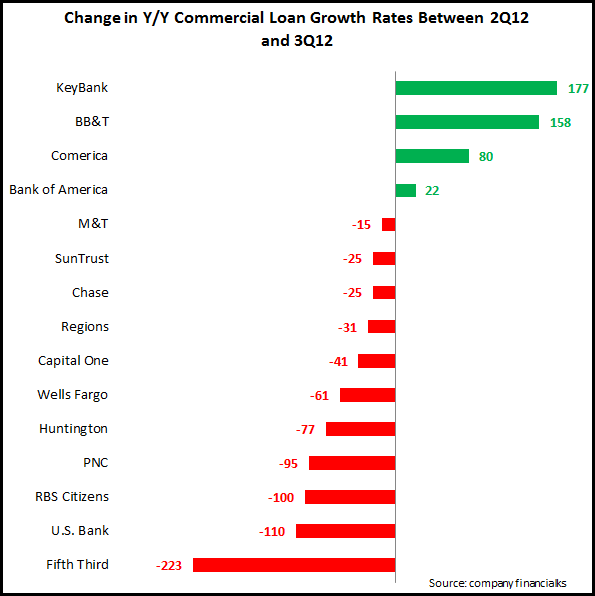
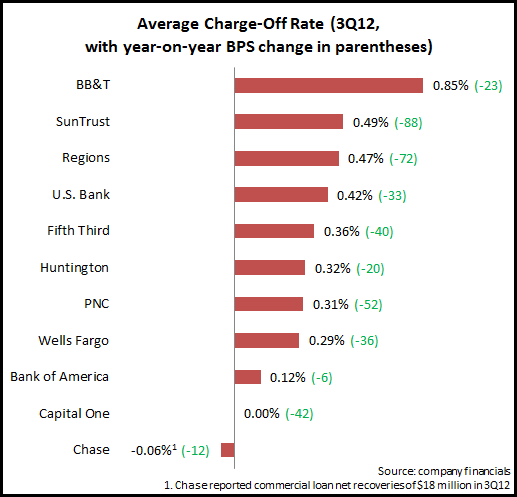
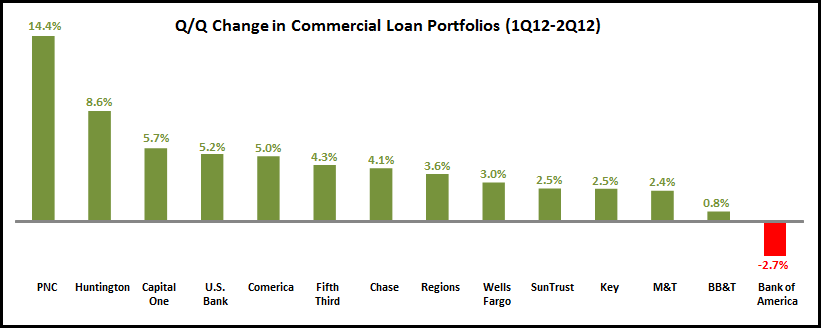
A noteworthy trend among large U.S. banks’ 3Q11 financials has been the significant rise in commercial lending. This continues a trend that has been evident in recent quarters. Of course, the current strong growth follows significant declines in commercial lending in 2008 and 2009 in the wake of the financial crisis.
Some of these banks have boosted overall commercial loan growth rates by targeting specific industry sectors. Comerica generated overall commercial loan growth of 21%, but grew its energy loan portfolio by 62% and its tech and life sciences portfolio by 36%. Other banks are following the industry targeting trend. Huntington recently launched a new energy lending initiative, and Associated Bank established a Healthcare Industry Banking Group.
It is notable, however, that uncertainty regarding the Presidential election and the looming fiscal cliff led to an overall 22 bps decline in y/y commercial loan growth rates between 2Q12 and 3Q12 for the 14 banks in our study, from 13.52% to 13.33%.
Although growth rates are robust, loan utilization rates remain relatively low, which can again be attributed to the economic uncertainty as well as many larger companies being flush with cash. The relatively low utilization rates indicate that commercial loans growth could accelerate once again if and when fiscal issues are resolved and economic confidence increases. And some banks are already seeing improved utilization rates:
- Comerica’s utilization rate was 48.2% in 3Q12, having hit a low of 44.2% in 1Q11.
- Regions’ utilization rate grew from 39.8% in 4Q10 to 44.4% in 2Q12.
Even as banks grow commercial lending, charge-off rates continue to decline. EMI’s analysis of charge-off data from 11 leading banks found an average commercial loan charge-off rate of 0.25% in 3Q12, down 29 bps year-over-year, and 11 bps from the previous quarter.
Finally, both low interest rates and increased competition continue to exercise downward pressure on commercial loan yields. Our analysis of yield data from 13 leading U.S. banks found that the average yield in 3Q12 was 3.81%, down 35 bps y/y and 19 bps q/q.