The major U.S. credit card issuers have now published their quarterly financials. A review of these reports by EMI revealed the following 10 trends:
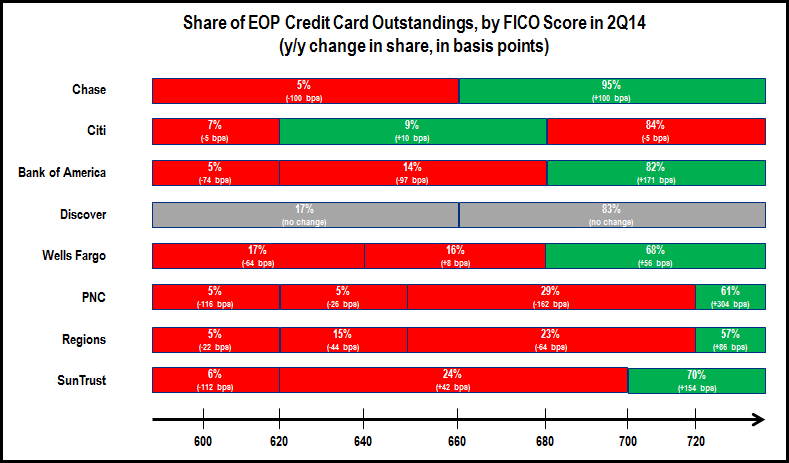
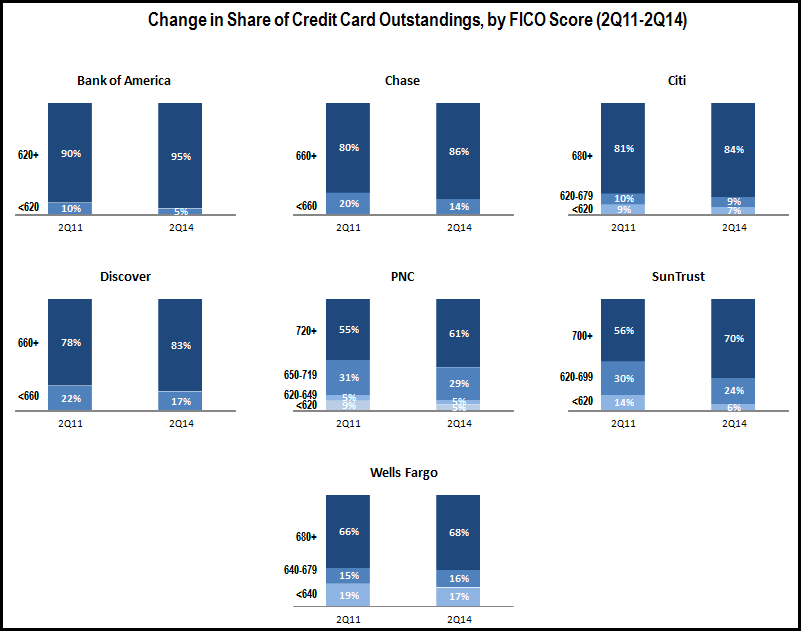
- Outstandings are growing. Credit card loan growth is once again being led by regional bank card issuers (such as SunTrust and Wells Fargo who tend to cross-sell cards to existing bank customers), as well as card “monolines” (such as Capital One and American Express). Banks with national credit card operations report lower growth (or even declines) as a result of the lingering effects from the financial crisis, runoff of promotional rate balances, as well as high payment rates. But even here we are seeing signs of growth: although Bank of America reported a 1% y/y decline in average outstandings, it also reported its largest quarter for new account origination since the fourth quarter of 2008.
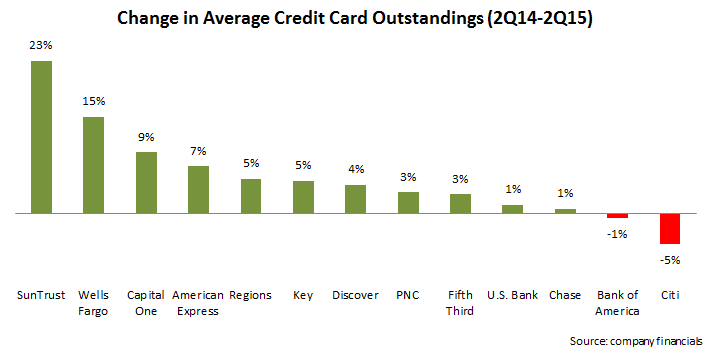
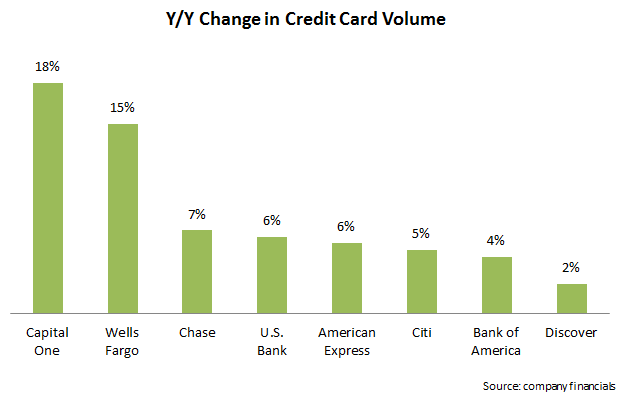
- Volume continues to grow, but with some slowdown. Some leading issuers continue to grow volume at double-digit rates (Wells Fargo grew loans and volume by 15%, boosted in part by the bank’s acquisition of the Dillard’s portfolio). Other issuers had lower volume growth, and many pointed to the impact of lower gas prices. For example, Discover reported volume growth of just 2%, but absent gas prices, this growth was 5%.
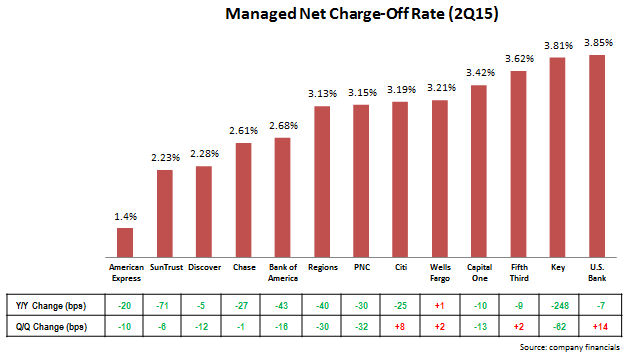
- Net charge-off rates continue to decline to historic lows. For many leading issuers, net charge-off rates are well below historic norms. In addition, the rates continue to decline; of the 13 issuers studied, 12 reported year-on-year charge-off rate declines.
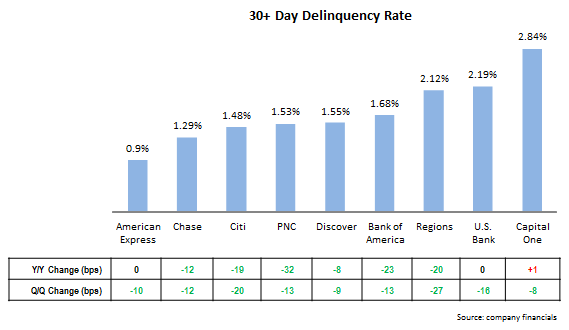
- 30+ day delinquency rates are also declining. Delinquency rates tend to be a leading indicator of future charge-offs, so it is notable that 30+ day delinquency rates continue to decline.
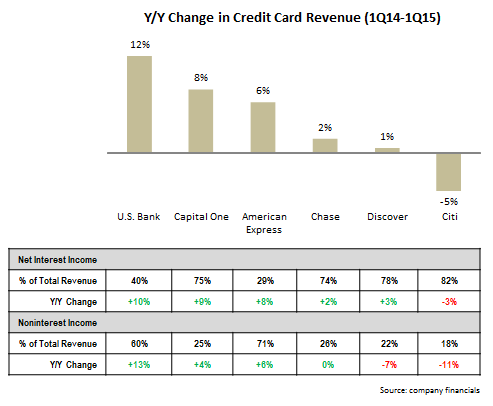
- The profit picture is mixed for issuers. Six leading issuers provide credit card profitability data, as they operate standalone payment units. Four of the six issuers reported y/y declines in profitability as growing expenses exceeded revenues. However, Chase increased net income for its Card Services unit by 33%, driven by lower costs (9% decline in noninterest expense, and 10% fall in provision for loan losses). American Express grew its U.S. Cards net income by 15%, as revenue growth of 6% and a 4% decline in provisions exceeded a 4% increase in noninterest expense.
- Growth in lending and volume are driving revenue growth. In the wake of the 2008 Financial Crisis and subsequent industry retrenchment, credit card industry revenues fell significantly. As the economy stabilized and then grew, leading issuers continued to struggle to attain revenue growth. Now the return to outstandings growth, as well as continued loan growth, is finally enabling issuers to increase revenues.
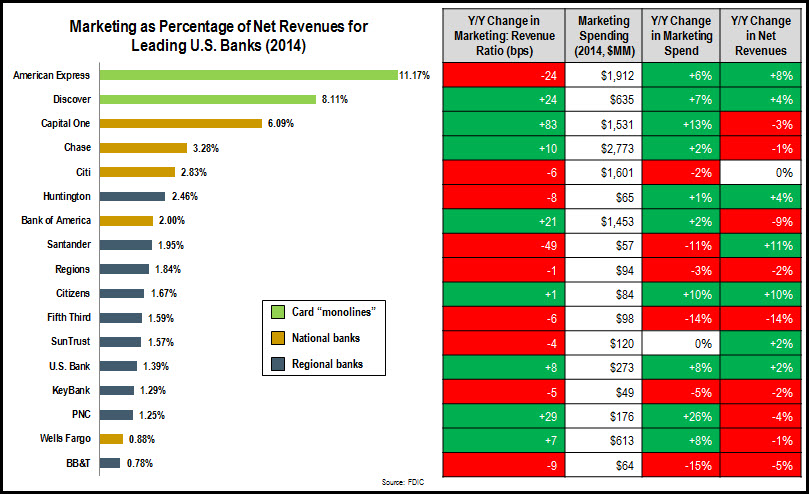
- To support this revenue growth, card issuers’ noninterest expenses are increasing. The rise in revenues is driving growth in expense areas like marketing and rewards costs. Of the five issuers providing noninterest expense data, four reported y/y increases, led by Discover (+18%) and U.S. Bank (+13%).
- Provisions for loan losses are (mainly) decreasing. As net charge-off and delinquency rates continue to decline, three issuers reported y/y declines in their provisions for loan losses. However, Capital One and U.S. Bank increased provisions, with Capital One growing provisions by 69%.
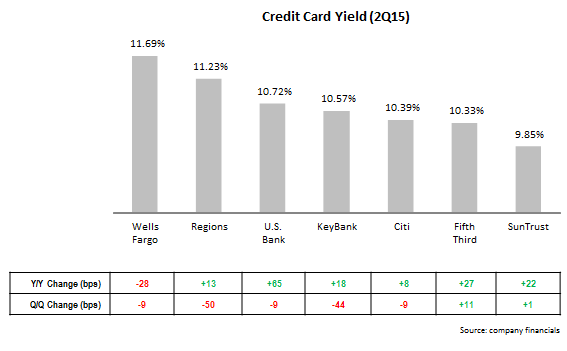
- Issuers are increasing credit card yield. Of the seven leading issuers who reported card yield in their financials, six reported y/y growth. The exception was Wells Fargo, which had the highest yield in 2Q15. However, five of the seven reported q/q declines; the exceptions were Fifth Third and SunTrust, which had the lowest yield among reporting issuers.
- Issuers are using a range of channels for new account acquisition. In general, cards issuers are continuing to reduce their dependence on direct mail for new card acquisition, and are focusing more investment on digital and branch channels. Chase reported that its online channel accounted for 62% of new card accounts in 2Q15. Even though Citi is continuing to cut its U.S. branch network, it reported that credit card acquisition via branches was up 10% on a same-store basis.