In a recent blog post, EMI discussed growth trends in credit card outstandings and charge-off rates, and the importance of ensuring that both remain at manageable levels. Now, our analysis of 2Q17 financials for leading issuers, as well as the latest reports from the FDIC and FFIEC, reveal the following trends on these two key credit card metrics:
- Issuers continue to report steady y/y growth in credit card outstandings, although the rate of growth has moderated in recent quarters. According to the FDIC’s Quarterly Banking Profile, credit card loans rose 4.5% to $780 billion. The growth rate was unchanged from the previous quarter, but marked a reduction from the 6%+ rates in the first three quarters of 2016.
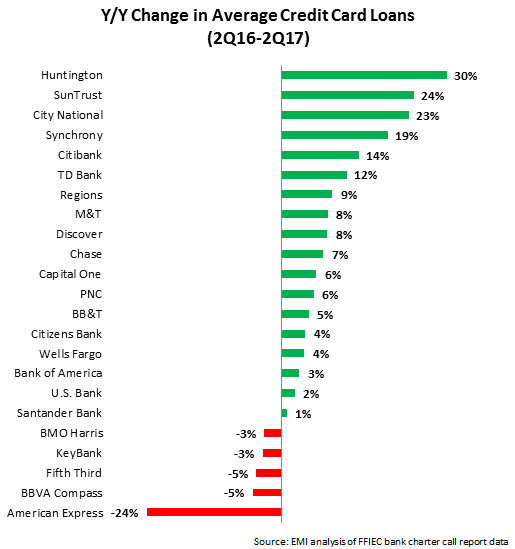
- According to FFIEC call reports, regional bank card issuers like Huntington, SunTrust and City National reported the strongest y/y growth rates in credit card loans in 2Q17. Leading issuers also generated steady credit card loan growth: Citibank (+14% y/y, boosted by the acquisition of the Costco portfolio), Chase (+7%), Capital One (+6%) and Bank of America (+3%).
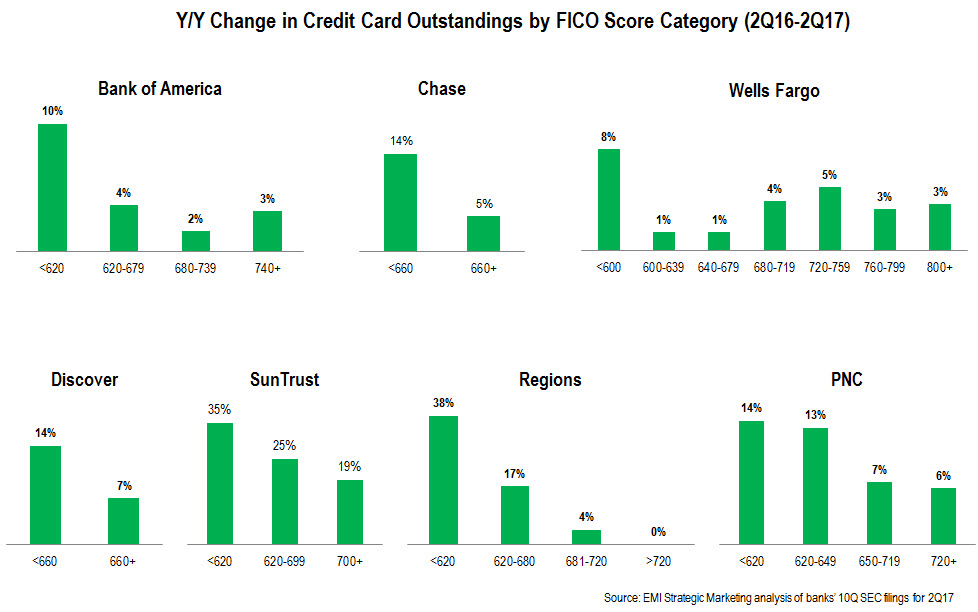
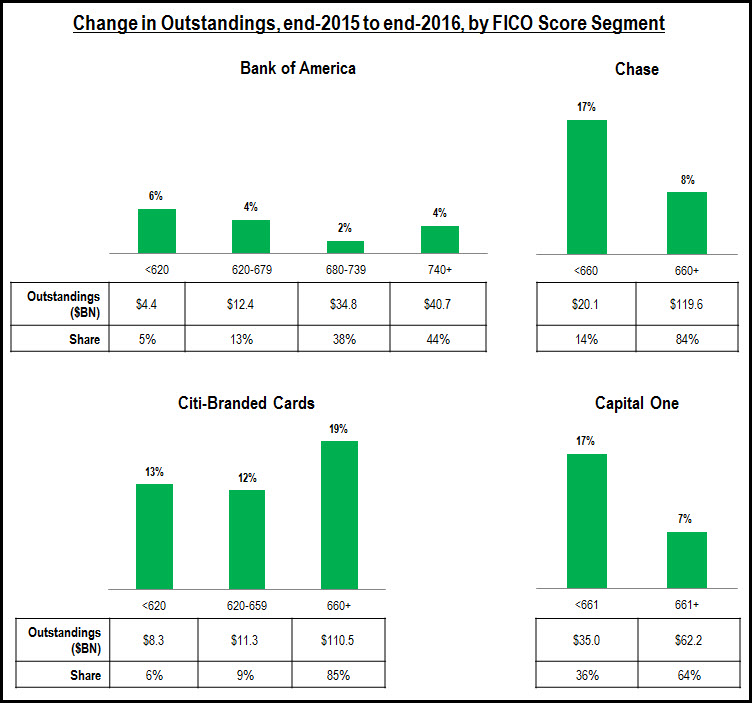
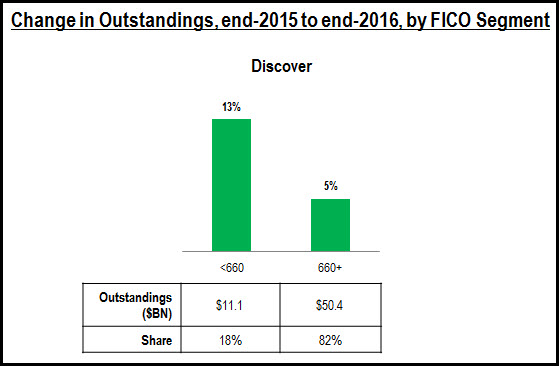
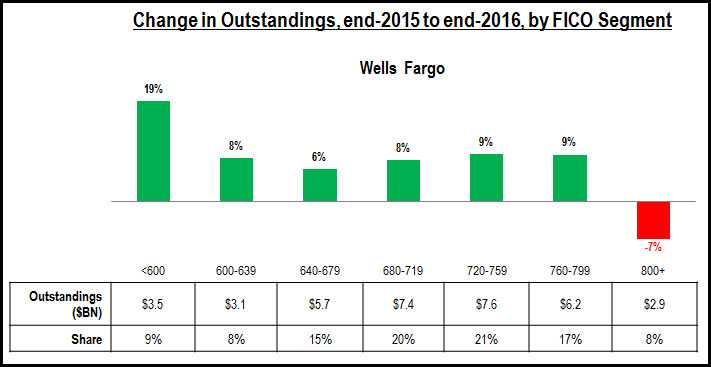
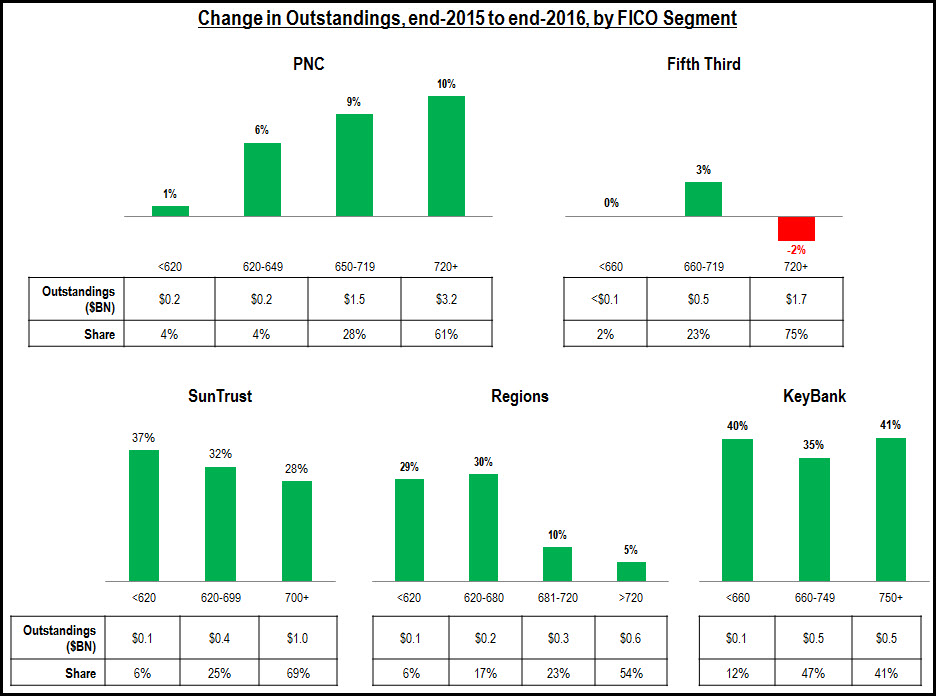
- Leading issuers are growing credit card outstandings across the FICO Score spectrum. Our analysis of selected credit card issuers’ 2Q17 10Q SEC filings found that issuers are reporting loan growth in all of their FICO Score segments, with most experiencing strongest growth in the sub-prime and near-prime categories. However, significant differences remain in the FICO Score composition of different card portfolios. For example, 35% of Capital One’s consumer credit card outstandings are held by people with a FICO Score of 660 or lower, but this segment only accounts for 12% of Chase outstandings and 14% of Citi’s portfolio.
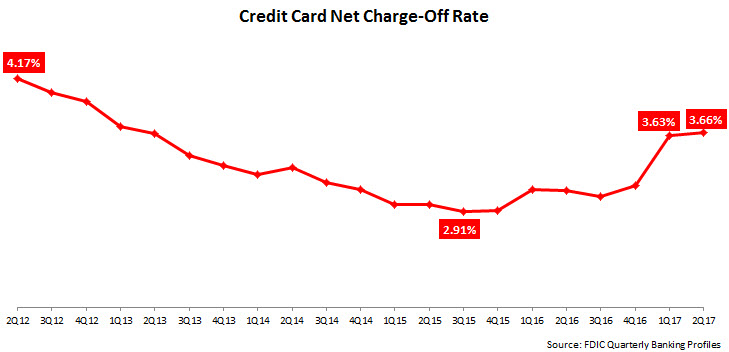
- The rise in credit card outstandings is being mirrored by continued growth in net charge-off rates. According to the FDIC Quarterly Banking Profile, the average charge-off rate was 3.66% in 2Q17. This marked a significant y/y rise of 55 basis points. However, the rate was only up 3 bps from the previous quarter, indicating a slowdown in the growth trajectory. Moreover, the current rate remains low by historic standards.