EMI analyzed 2018 marketing spend by 27 of the leading U.S. banks, and found that most banks are ramping up their investment in marketing. The rise in marketing budgets is driven by a number of factors, including:
- The continued growth of the U.S. economy.
- The ongoing scaling back of bank’s branch networks. This reduces their on-the-ground presence, so banks need to invest more in marketing to maintain brand awareness. In addition, cost savings from smaller branch networks can be redirected to other functions, including marketing.
- The need for established banks to reposition themselves in a changing financial services ecosystem, characterized by the emergence of fintech firms and direct (branchless) banks.
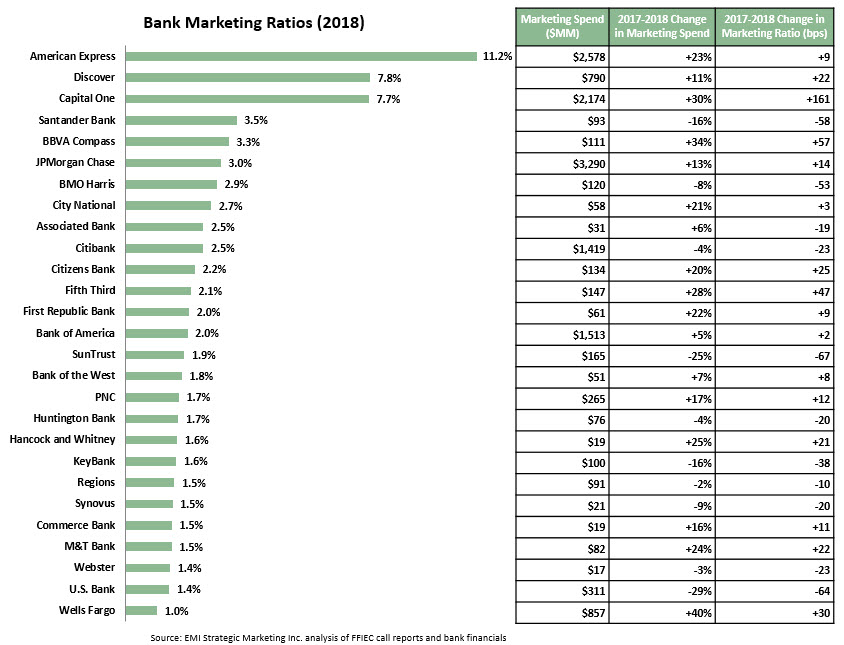
Overall, marketing spending by the banks rose 13% to $13.0 billion in 2018.
- 17 banks grew their marketing budgets.
- 14 banks increased their marketing spend by double-digit rates, led by Wells Fargo (+40%), BBVA Compass (+34%) and Capital One (+30%).
5 banks spent more than $1 billion on marketing: JPMorgan Chase ($3,290MM), American Express ($2,578MM), Capital One ($2,174MM), Bank of America ($1,513MM) and Citibank ($1,419MM).
The 27 banks’ cumulative marketing spend represented 2.9% of their 2018 net revenues, which represents a 17 basis point rise from the banks’ 2017 marketing ratio.
- The marketing ratios of the 27 banks ranged from 11.2% for American Express to 1.0% for Wells Fargo.
- A majority of the banks (16 of the 27) had marketing ratios in the 1.5% – 2.5% range.
The variation in marketing ratios is due to on a number of factors, including product concentration, size of branch networks, perceived importance of strong brand equity, as well as the timing of marketing investments (such as the launch of new advertising campaigns).
- For example, American Express and Discover have no branch networks, are primarily focused on selling credit and charge cards, and have traditionally invested to maintain strong brand awareness. Therefore, their marketing ratios are more in line with fast moving consumer goods firms, rather than financial institutions.
15 banks increased their marketing ratios between 2017 and 2018.
- Wells Fargo, which has traditionally had a low marketing ratio as it focused resources of its large branch network, increased its marketing spend by 40% to more than $850 million in 2018, and its marketing ratio grew by 30 bps. The strong rise in spend was in large part due to the launch of the “Re-Established” integrated marketing campaign in May 2018. It is worth noting that Wells Fargo remains well below national bank peers, such as JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America.
- Other banks with strong increases in their marketing ratios include Capital One (+161 bps to 7.7%) and BBVA Compass (+57 bps to 3.3%).