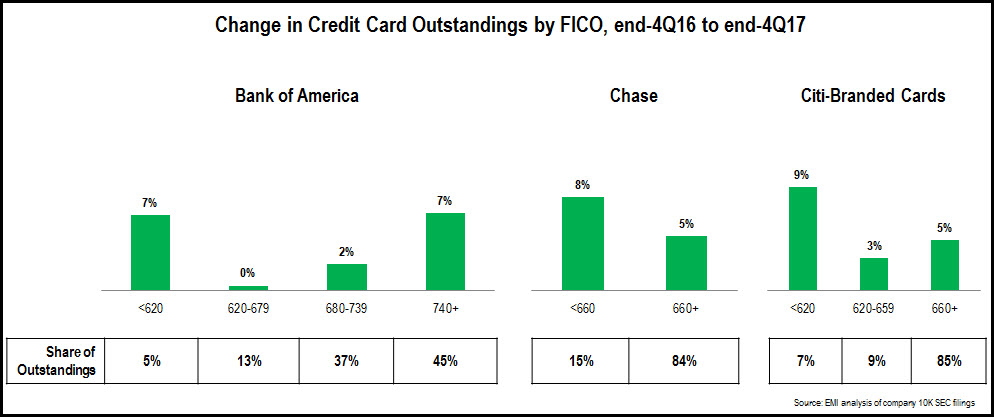
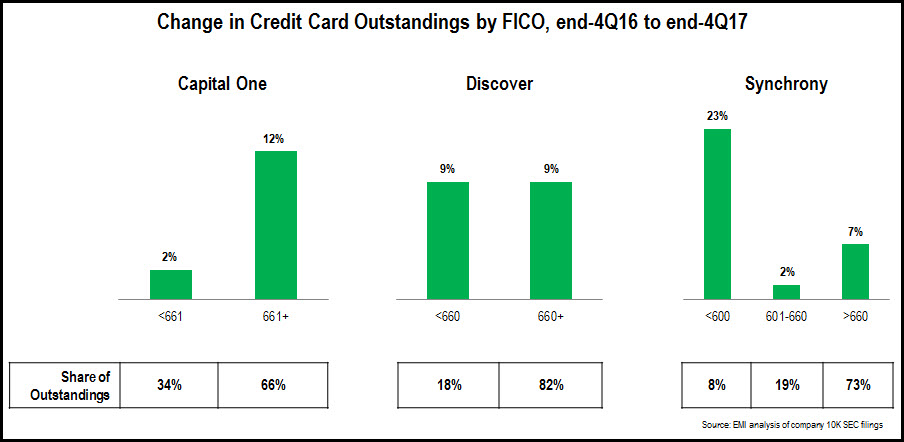
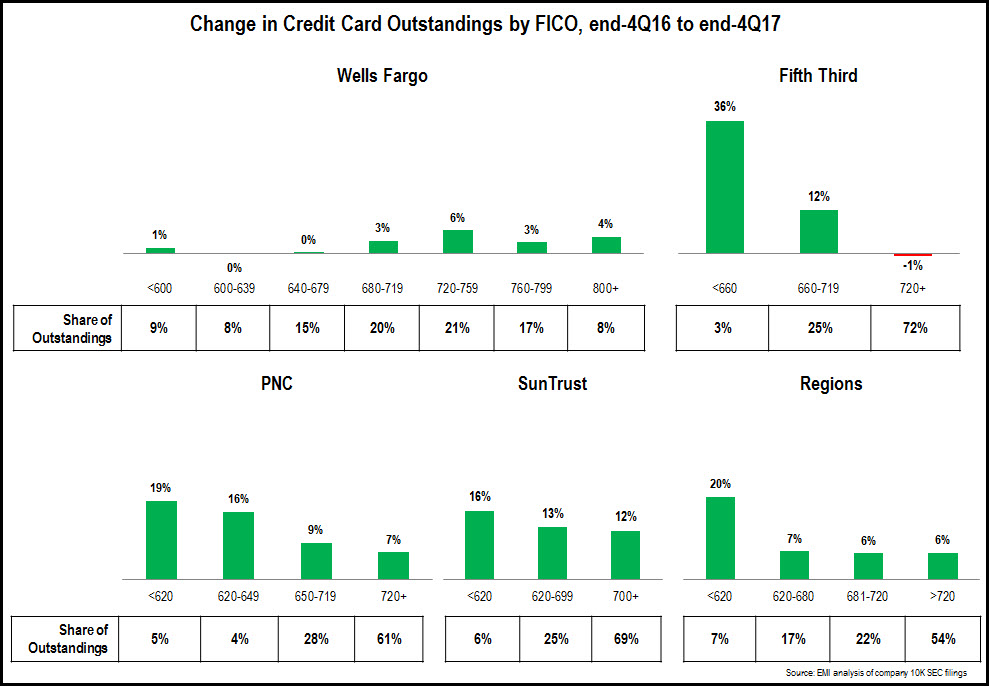
A detailed analysis of FFIEC call reports revealed that leading banks significantly reduced their advertising and marketing expenditure in 2020. However, as the economy rebounds strongly from the economic downturn caused by the coronavirus pandemic and increased competition from new entrants, banks seem poised to ramp up their marketing spending in the second half of 2021 and beyond.
Change in Marketing Spending Between 2019 and 2020
EMI Strategic Marketing studied data from 28 leading banks and found a 17% decline in advertising and marketing budgets, to $451 billion. This decline follows increases of 7% in 2019 and 15% in 2018.
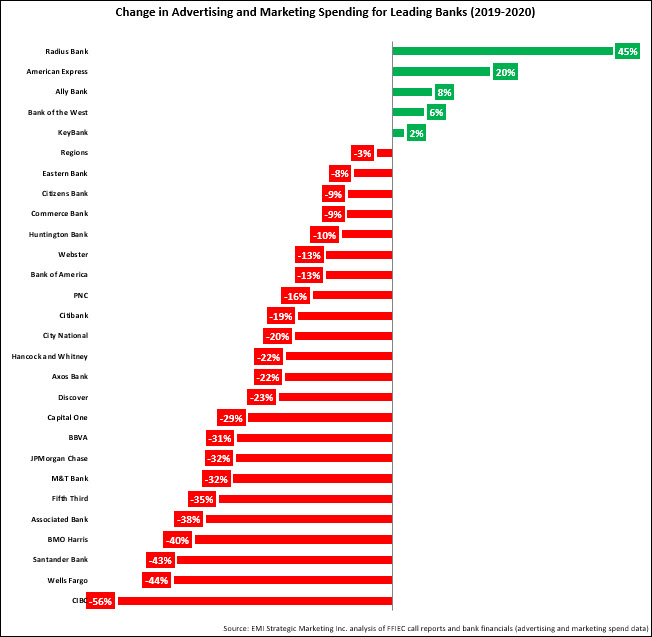
Although most banks cut their marketing budgets, some banks bucked this trend, actually increasing their 2020 marketing spending:
- Most notable in this regard was American Express, which at nearly $3.5 billion already has the largest advertising and marketing budget among leading U.S. financial firms. It spent $1 billion in 4Q20 alone as it ramped up investments in new card acquisition. Furthermore, it plans to continue this investment and recently reported that it could spend up to $4.5 billion in marketing in 2021.
- Direct bank Ally Bank launched a new online advertising campaign in September 2020, which contributed to an 8% y/y increase in its marketing spend, to $161 million.
- Challenger bank Radius Bank increased its advertising and marketing budget by 45% to $1.9 million in 2020, although its marketing ratio fell from 2.6% to 1.7% as its revenues jumped by 127%. (Radius Bank was recently acquired by LendingClub.)
It is also worth noting that some banks cut marketing budgets in 2020 following a ramp up in spending the previous year. A good example is BBVA, which grew its marketing budget from $83 million in 2017 to $111 million in both 2018 and 2019 as it changed its brand name from BBVA Compass to BBVA. It then cut the budget back to $76 million in 2020.
With Wells Fargo cutting its budget by 45% to $600 million, it reduced the number of banks with billion-dollar marketing budgets to five (American Express, JPMorgan Chase, Capital One, Bank of America and Citi).
Trends in Bank Marketing Ratios
The average 2020 marketing ratio was 2.8%, down more than 40 basis points from 2019, and back at levels seen in 2017.
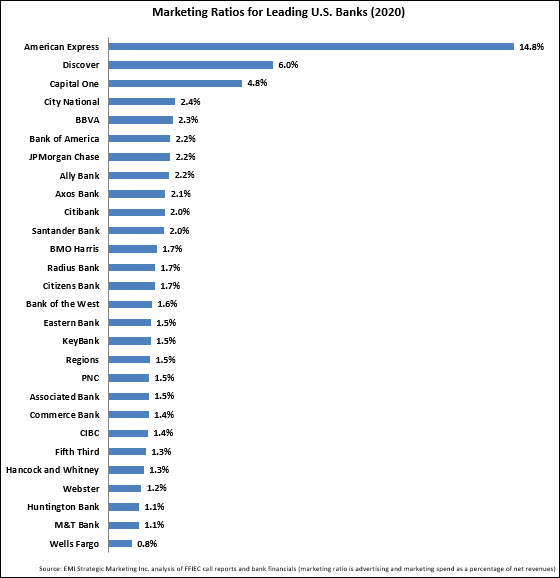
Only 3 of the 28 banks – American Express, Ally and Bank of the West – increased their marketing ratios in the past year.
American Express and Discover – which have national card franchises that account for a significant percentage of assets and do not have to support branch networks – have the highest marketing ratios. Capital One’s marketing ratio is a mix of its card unit (6.8%) and retail bank unit (3.1%). Regional banks tend to have marketing ratio of 1% to 3%.
It is interesting that digital banks like Ally Bank, Axos Bank, Radius Bank and CIBC U.S. – which like American Express and Discover do not have to support branch networks – have marketing ratios that are in line with their regional bank competitors. This can be attributed to a number of factors, including devoting significant time and resources into improving the digital experience rather than brand advertising.
Bank Marketing Spend Trends for 2021
Looking forward to 2021, we expect that bank marketing spend will recover as the economy gradually reopens following COVID-19 (The Congressional Budget Office expects real GDP to return to pre-pandemic levels by mid-2021). Many banks have signaled their intent to increase their marketing spending in 2021. JPMorgan Chase stated that it expects marketing spend to return to pre-COVID levels in 2021. And while Citi’s marketing spend fell by 20% in 2020, it actually grew spending 2% y/y in 4Q20.
Bank marketing budgets will be impacted by growing merger and acquisition activity in the industry. Mergers that are expected to be completed in 2021 include First Citizens and CIT, Huntington and TCF Financial, PNC and BBVA USA, and M&T Bank and People’s United. Merging banks typically highlight long-term cost savings, but there will be a critical short- to medium-term need for marketing investment as they create new branding, launch new advertising campaigns, update branch signage, and revamp digital and social media channels).
While overall bank marketing spend is likely to recover in 2021, the composition of marketing budgets should change, in particular due to banks investing more in digital and social media marketing channels to match customer preferences and behavior. In addition, banks will be developing new messaging to address post-pandemic financial challenges and to communicate an effective and consistent experience across all their service channels.