All of the main U.S. credit card issuers have now reported second quarter 2011 financials, which reveal some interesting trends:
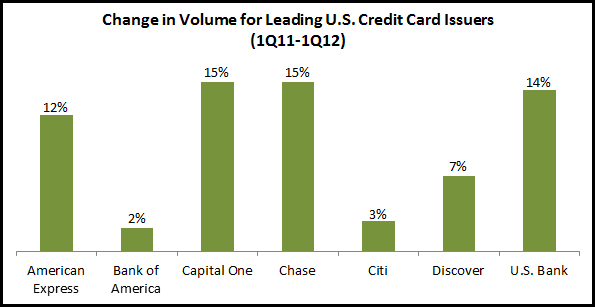
Volumes: In recent quarters, card purchase volumes have grown significantly as issuers have focused attention on positioning cards as spending rather than lending tools. Most issuers continued to grow volumes in 2Q12, although in some cases, the rate of growth was lower than in recent quarters. Wells Fargo (+15%), U.S. Bank (+13%), Chase (+12%) and Capital One (+11%, excluding the impact of the HSBC portfolio acquisition) all reported double-digit year-on-year spending increases. American Express, which has typically led the industry in volume growth, reported a y/y rise in spending of 9%, down from 12% in 1Q12. And both Bank of America and Citibank reported no growth in purchase volumes. Issuers will continue to push volume growth in the coming quarters, as they continue to seek to take payments share from cash and checks.
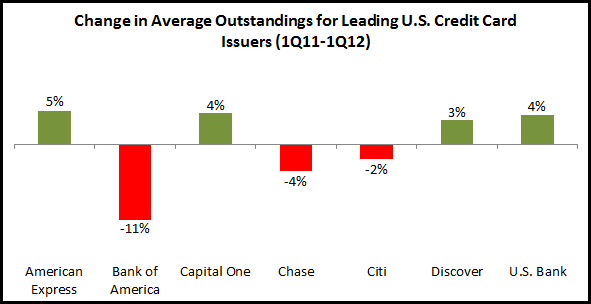
Outstandings: In recent years, issuers reacted to the financial crisis by significantly deleveraging their credit card portfolios. Now there are signs that this process has bottomed out and a number of issuers are growing outstandings. The largest portfolios continue to decline, with Bank of America (-10%), Citibank (-3%) and Chase (-1%) all reporting year-on-year declines in end-of-period outstandings. On the other hand, banks with smaller portfolios reported y/y growth, including SunTrust (+39%), PNC (+10%), Wells Fargo (+7%), U.S. Bank and Fifth Third (both +5%). In addition, American Express (+5%) and Discover (+4%) both grew outstandings. The prospects for outstandings growth in the industry in general in the quarters will be dependent on general economic conditions, as well as the extent to which issuers want to push loan growth in order to grow revenues.
Charge-Off and Delinquency Rates: As issuers reduced outstandings following the financial crisis in 2008, they also set about tackling charge-offs, which spiked spectacularly in 2008 and 2009. Charge-off rates have declined significantly over the past two years, and in many cases are now below normalized levels. There has been a widespread expectation in recent quarters that the sharp declines in charge-off rates would bottom out; however, the most recent quarter continued the pattern of charge-off rate declines. All of the main issuers reduced charge-off rates by more than 100 bps y/y, and only one main issuer (U.S. Bank) reported a q/q increase in its charge-off rate. American Express, Discover and Capital One reported charge-off rates below 3% in 2Q12. Bank of America remains the issuer with the highest charge-off rate (at 5.27% in 2Q12), but it is notable that this rate is down from levels of more than 14% in 2009. There is an expectation that charge-offs will continue to decline in the coming quarter, given that delinquency rates (which are an indicator of future charge-offs) are also continuing to decline. Some issuers are anticipating that credit quality indices will bottom out or even grow, in particular if the issuers relax underwriting standards to grow outstandings. So, a number of leading issuers are increasing their provision for loan losses.
Revenue: This remains the big negative for issuers, with downward pressure on both net interest income (for those issuers who are continuing to experience outstandings declines) and noninterest income (from the ongoing impact of the CARD Act, which makes it more difficult to generate fee income). Issuers with lower outstandings (Bank of America, Citibank and Chase) reported revenue declines, but issuers who grew outstandings in 2Q12 managed to grow revenues. American Express increased revenue 5%, with net interest income rising 6%. Discover grew total revenues 6%, with a 4% decline in noninterest income more than offset by a 10% growth in net interest income. Prospects for revenue growth in the coming quarters will be very much dependent on the ability to grow outstandings, given the limited scope for generating fee income.