The leading U.S. credit card issuers continued to exhibit trends that have become established in recent quarters, but there were also some signs of change:
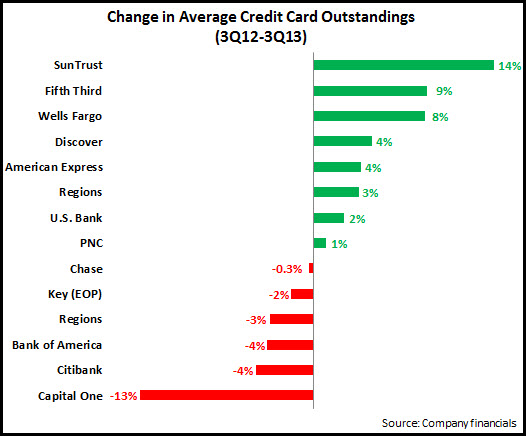
- Outstandings: Average credit card outstandings continued to decline y/y, with the big four issuers (Chase, Bank of America, Citibank and Capital One) reporting portfolio decreases. However, both credit card “monolines” (American Express and Discover) and some regional bank card issuers reported relatively strong growth. Even among the big three issuers, there were indications of growth: Chase reported a 6% y/y rise in new accounts (1.7 million); and Bank of America new accounts rose from 850,000 in 3Q12 to more than 1 million in 3Q13.
- Volume: Reflecting the change in the industry in recent years from a lend-centric to a spend-centric model, most issuers reported strong y/y volume growth. Wells Fargo volume rose 14%, as new accounts grew 11% and credit card penetration of its retail bank households increased to 35%. And it is looking to further propel volume growth with its recently-launched rewards program. Bank of America and Chase also translated strong new account generation into double-digit volume growth. Discover had relatively low volume growth of 3%, but is aiming to increase volume and outstandings at the same rate.
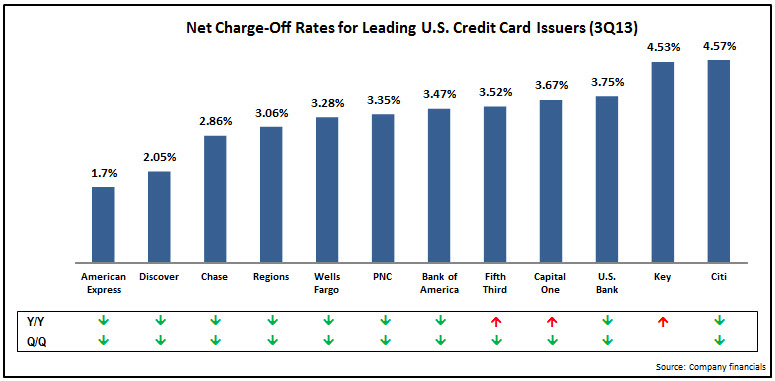
- Credit quality: charge-off rates continue to decline for most issuers. Of the 12 issuers who provided charge-off rate data, 10 have rates below 4%, and three issuers (American Express, Chase and Discover) have rates below 3%. As a result, provisions for loan losses continued to fall for most issuers, which boosted profitability. For 30+ day delinquency rates, issuers reported y/y declines, but q/q increases.
We expect that, as the economic recovery continues, consumer confidence will grow, as will their willingness to take on credit card debt. This may lead to increases in charge-off rates from these historically low levels, but issuers will feel that the resulting growth in noninterest and net interest income will more than offset any rises in provisions for loan losses and noninterest expenses, such as marketing costs.
However, as issuers look to ramp up credit card marketing, they need to factor in the fundamental changes in consumer perceptions and usage of their credit cards. These changes impact various elements of the marketing mix, including:
-
Positioning: Following the financial crisis, issuers shifted away from positioning credit cards as easy ways to access credit, and towards credit cards as an efficient payments method. As consumer demand for credit recovers, issuers may need to adapt positioning once again to have a balance between a lend-centric and spend-centric focus.
-
Product: Issuers continue to target more affluent cardholders, so they will need to have a card portfolio that is appropriate for this market. This explains why both Wells Fargo and U.S. Bank recently entered into card-issuing deals with American Express.
-
Pricing: As the CARD Act places many restrictions on issuers’ ability to change APRs, we expect that there will not be huge price competition in APRs, but rather the focus will be on lengthy zero-rate introductory offers, in particular on balance transfers.
-
Loyalty: Issuers will continue to enhance rewards programs (and accompanying offers) to drive activation, retention and ongoing spending. To maintain control over costs, issuers are looking to develop more merchant-funded programs, and this trend may gain traction as issuers develop mobile wallets that will enable consumers to manage loyalty programs on their smartphones as well as receive specific merchant offers at the point of sale.
-
Channel: There has been much coverage of the fact that branches are rapidly losing share for everyday banking transactions. Many banks are looking to redefine the role of the branch, in particular to leverage its potential as a key sales channel. Wells Fargo recently reported that 80% of new card accounts are opened in its branches. The online channel has also become a key credit card sales channel: Chase reported that 53% of new credit card accounts were acquired online in 3Q13.