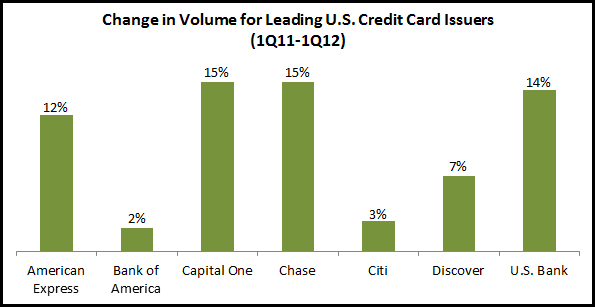
First quarter 2012 results of the leading U.S. credit card issuers reveal that they are continuing to drive spending growth by cardholders. Four of the seven leading issuers reported double-digit year-on-year growth rates, led by Chase and Capital One at 15%, followed by U.S. Bank at 14% and American Express at 12% (American Express also reported that small business card volume rose 16% y/y, its highest growth rate since before the financial crisis. In contrast, Bank of America and Citi had anemic – albeit positive – growth rates.
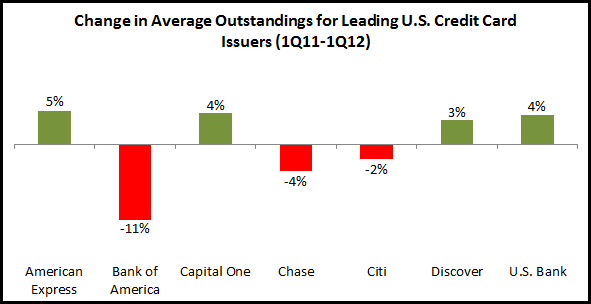
The situation with regard to lending growth is more mixed. With the return to economic growth, and the significant improvement in credit quality, issuers have been looking to increase outstandings. However, consumers still bear the scars of the financial crisis and remain reluctant to increase their card borrowing. In addition, many issuers have not yet significantly relaxed the stricter underwriting standards that came into place in 2008 and 2009. The three largest issuers (in terms of outstandings) all reported y/y declines, with Bank of America’s average loans falling 11%. Bank of America’s average U.S. credit card outstandings have declined almost 22% over the past two years, and fell below $100 billion in the most recent quarter. (It should be noted that this decline is partly attributable to card portfolio sales, with the bank selling portfolios over the past year to Regions, Sovereign and Barclaycard.) Bank of America and Citi were the two issuers with declines in both volumes and outstandings. Chase also reported a y/y decline in average outstandings, but this was due to the sale of the Kohl’s private label portfolio in the first quarter of 2011.
So, at first viewing, we see some credit card portfolio retrenchment among those banks like Bank of America and Citi that were hardest hit by the financial crisis, while other leading issuers are now growing their portfolios. However, at closer inspection, Bank of America and Citi are also positioning themselves for future card growth. Citi had credit card account growth for the fourth consecutive quarter. And Bank of America reported that new accounts in 1Q12 were up 19% y/y.
In addition, it is notable that Bank of America is changing the composition of its card portfolio by selling off some private-label card portfolios and changing how cards are originated. (It reported that half of the 800,000 cards originated in the first quarter came through its branch channel.)