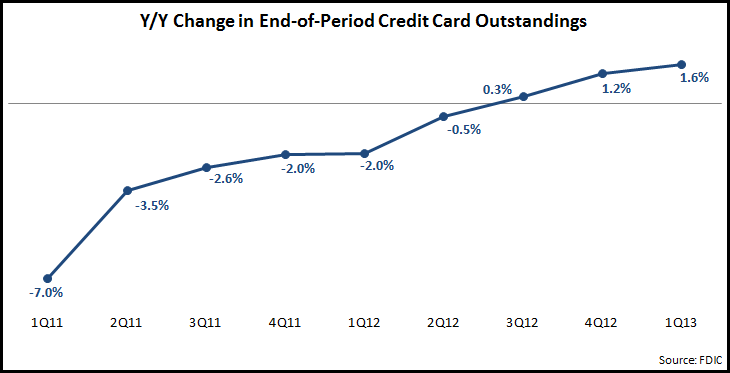
EMI’s analysis of recently-published U.S. bank data by the FDIC reveals that credit card outstandings rose 1.6% y/y to the end of 1Q13. Outstandings have been recovering in recent quarters, following a protracted period of declines as a result of the 2008 financial crisis. In addition, net credit card charge-offs continue to decline, falling 12% y/y in 1Q13.
Our analysis also finds that:
- 1,238 U.S. banks (19% of the total) have card assets, with 6% of banks having more than $1 million in card assets. 55 banks have more than $100 million in outstandings, with just 23 banks holding more than $1 billion in credit card loans.
- Of the 55% with more than $100 million in assets, 31(56%) reported increases in their credit card loan portfolios between end-1Q12 and end-1Q13
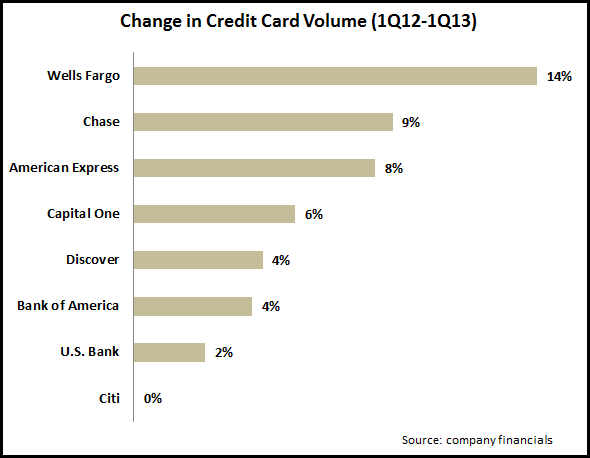
- The three largest credit card issuers–Citibank, Chase and Bank of America–all continued to report credit card loan declines, as they continue to deleverage. The cumulative decline for these three issuers was 5%.
- The former “monolines”–American Express, Discover and Capital One–all increased outstandings. Capital One reported a 44% increase, largely due to the acquisition of the HSBC card portfolio. American Express grew credit card loans 6%, with Discover’s outstandings rising by 7%.
- Many regional banks continued to increase credit card lending, albeit from significantly lower bases than their national bank counterparts.
- Some regional banks reported huge growth rates due to portfolio acquisitions. KeyBank acquired the Key-branded card portfolio from Elan Financial Services in August 2012, while TD Bank announced the acquisition of the Target card portfolio in October 2012.
- Other regional bank card issuers reported strong organic growth: SunTrust grew outstandings 16% to $614 million. Wells Fargo increased card loans 10% to $24.1 billion, as it increased its credit card household penetration rate to 34%.
- A few regional banks did register credit card loan declines, including Regions (-10%), U.S. Bank (-2%), PNC (-0.4%)
These trends in credit card outstandings–slow overall growth, declines among the big three issuers, growth for monolines and regional banks–are consistent with industry predictions that EMI published in a blog earlier this year.