For decades, bank branches have been focused on everyday banking transactions. However, with electronic self-service channels now handling a dominant share of these transactions, branches have come under intense scrutiny, with many industry commentators predicting the decline and even extinction of the branch channel. This view has been strengthened by the fact that banks are focusing significant attention on cutting costs in an era where revenue growth remains elusive. And branches represent a significant cost for banks.
Banks are belately beginning to react to this new environment by developing new branch strategies that recognize its changing role. Banks are now putting less emphasis on the branch as a channel for day-to-day financial transactions. Instead, branch investments are being directed to capture the potential of the branch as a key channel for sales, customer relationship development (through the provision of complex and/or sensitive financial advice), and branding (even customers who bank online tend to want the physical reassurance of the branch). In addition, banks are increasingly aware of the research value of branches, both in terms of directly surveying branch visitors as well as testing new product or service innovations in selected branches before full roll-outs.
Some examples of new bank branch strategies:
- In a presentation this week at the Morgan Stanley Financials Conference, PNC outlined a vision of its branch network that involves a more dynamic definition of branches, which includes multiple physical formats, as well as greater integration with both remote sales people and electronic channels.

- Huntington recently reported branch plans driven by both the desire for cost savings (closing traditional branches and opening in-store branches) as well as to leverage the latest technology (such as branch image capture and processing) to drive efficiency.
- U.S. Bank has three branch models, which enables the bank to tailor branch investments to market composition and opportunity.

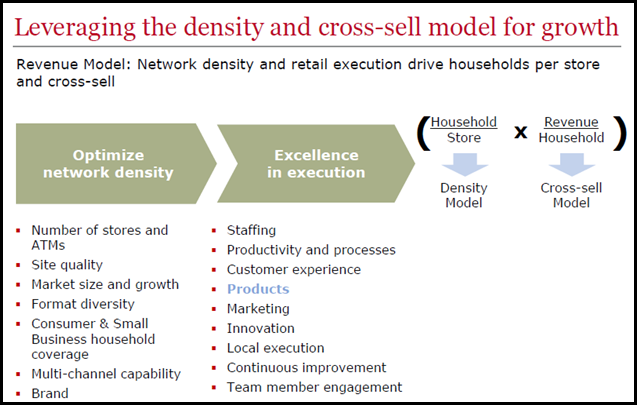
- Wells Fargo continues to have a strong commitment to the branch channel, as it claims that the vast majority of financial products are bought in a branch. It follows a specific model for branch productivity that is based on both in network density and retail execution, and which is seen in the following chart from its recent Investor Day:
- At its 2012 Investor Day, Chase discussed a number of branch innovations designed to reduce costs and improve the customer experience. These include self-service tellers, paperless tellers, instant-issue cards and access to remote sales specialists through video. It is testing other innovations like next-generation ATMs, paperless sales, and mobile demonstration zones. Chase is also continuing to deploy additional sales personnel in branches; at the end of 1Q12, Chase had more than 6,000 sales specialists (y/y increase of 21%).
As electronic channels continue to change how consumers and businesses interact with their banks, many banks are reassessing the level and type of investments in their branch networks. Though most are still committed to the branch model—noting its importance in sales and understanding that many customers still want to have the reassurance of a physical presence—the role of the branch is evolving and this has important implications for issues like branch sizing, design, staffing, technology deployment, and merchandising, as well as integration with other channels.
Subscribe