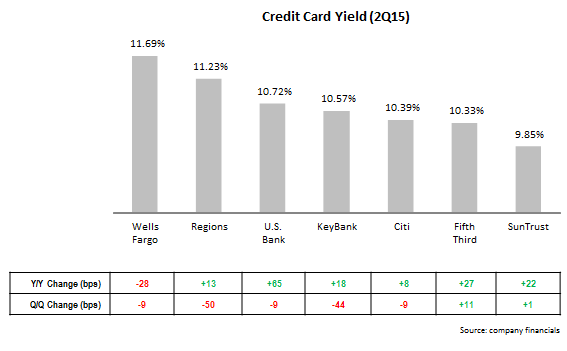
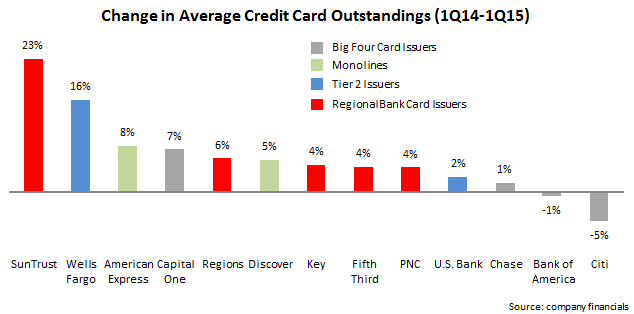
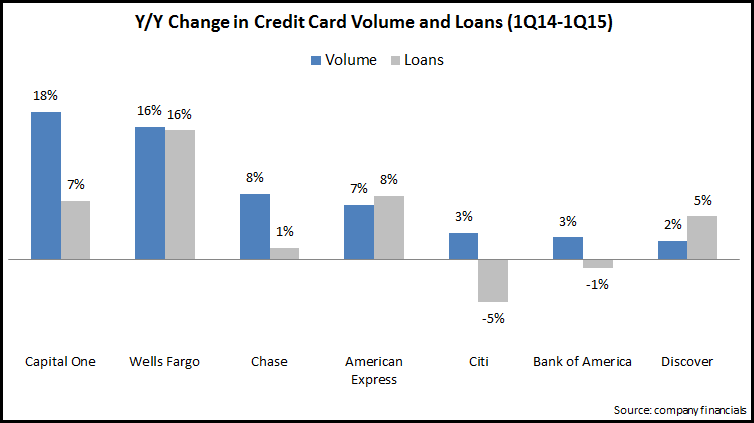
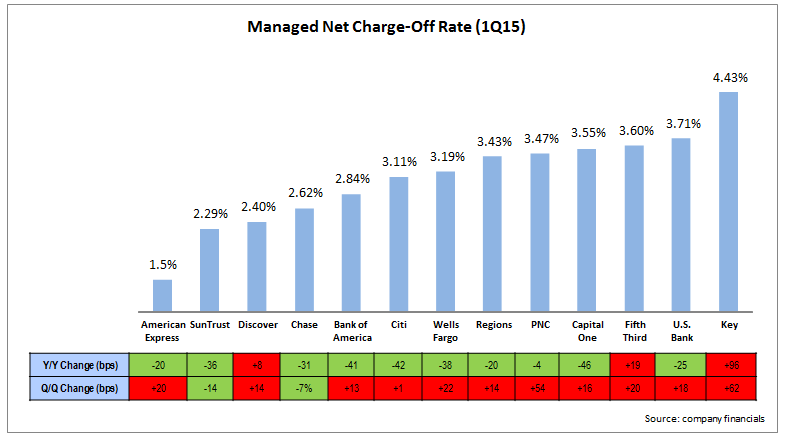
The Wall Street Journal recently reported that credit card outstandings may reach the $1 trillion threshold in 2016, for the first time since before the 2008 Financial Crisis. This is mainly due to overall economic growth and the rise in employment. Issuers are now increasing their focus on growing outstandings by making aggressive acquisition-and-activation offers (American Express is currently offering a bonus of up to $300 on its Blue Cash Everyday Card), promoting lengthy introductory offers, and increasing credit lines for existing cardholders.
A big question for issuers is, should they concentrate efforts on particular FICO score segments, or seek to drive growth across the FICO score spectrum? In the aftermath of the Financial Crisis and the resulting huge spike in charge-off rates, many leading issuers narrowed their focus, concentrating on the high-FICO score affluent segments, and ignoring subprime and low-prime consumers. However, as the economy has continued to recover, at appears that some issuers have renewed interest in the lower-FICO score categories.
EMI’s analysis of leading issuers’ 1Q16 SEC filings reveals that issuers are following different approaches:
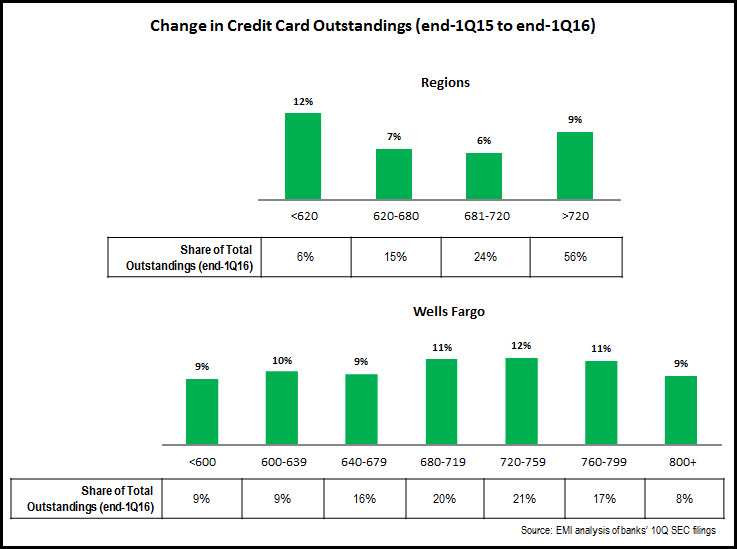
1. Growing outstandings across all FICO score segments. Regional bank card issuers like Wells Fargo and Regions have relatively strong growth across all FICO score segments. It is notable that the <600 subprime segment accounts for 9% of Wells Fargo’s outstandings, a higher percentage than for other issuers. Wells Fargo issues a subprime card and recently incorporated a free FICO score into its mobile banking app.
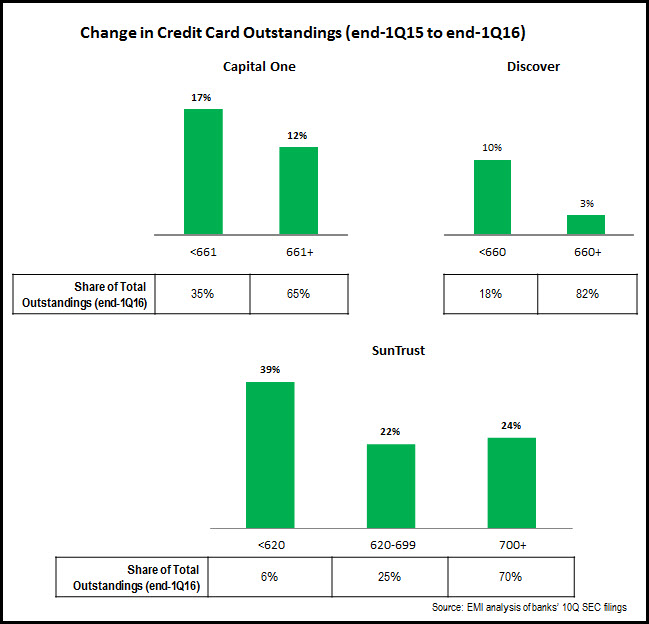
2. Generating stronger outstandings growth in low-FICO score segments. Capital One, Discover and SunTrust all have markedly strong growth rates in outstandings for low-FICO segments. 35% of Capital One’s outstandings come from the <660 FICO segment, whereas this segment accounts for only 18% of Discover’s outstandings. Discover grew <660 outstandings by 12% (to $10.0 billion), and it is worth noting that Discover launched the Discover it Secured Card in January 2016. SunTrust grew its <620 FICO portfolio by 39%, although this was coming from a low base of just $45 million.
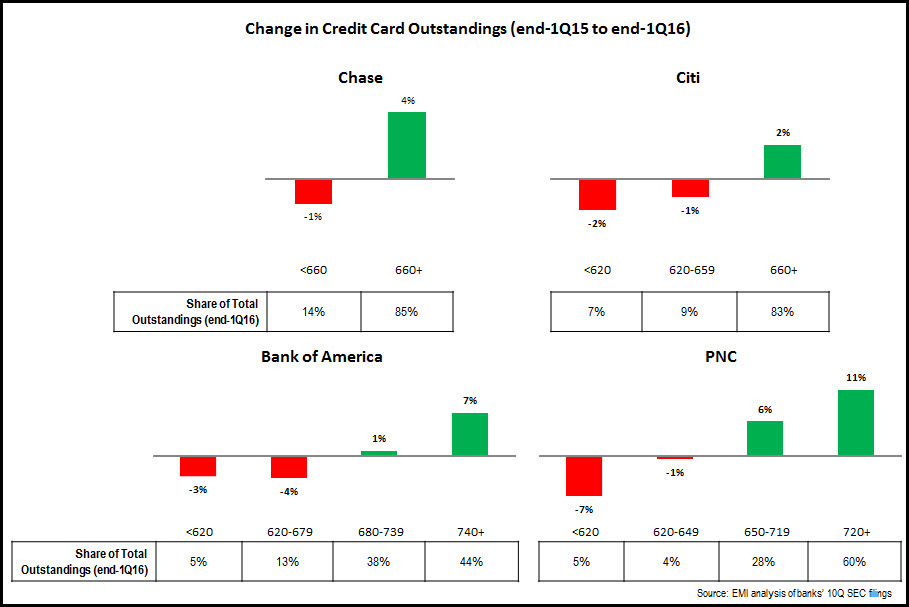
3. Continuing to focus outstandings growth on higher FICO score segments. The three largest issuers—Chase, Citi and Bank of America—all continue to experience declines in outstandings in their lower FICO score segments, which is offset by growth in higher FICO score categories. Regional bank card issuer PNC also follows this pattern.
As issuers look to continue to grow outstandings (and appear to be willing to let charge-off rates rise from their current low levels), they will need to develop approaches to target the different FICO score segments, including:
- Ensuring they have products in place to target different FICO score—and demographic—segments.
- Developing messaging, pricing, acquisition/activation offers and ongoing incentives to both attract new cardholders and encourage existing cardholders to increase their spending and borrowing
- Creating tools (such as free FICO scores) to educate consumers on understanding how their credit scores are determined and how they can practice good credit management