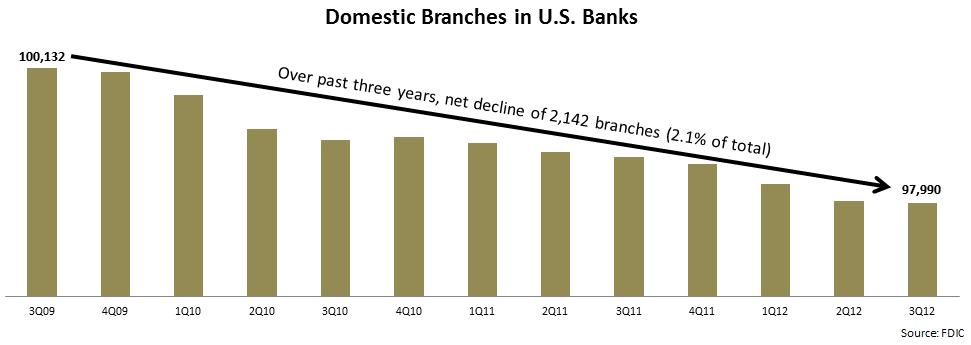
An EMI analysis of recently-published quarterly bank data by the FDIC found that U.S. banks are continuing to reduce branch numbers.
U.S. branches are very heavily concentrated in a limited number of banks:
- Just 50 banks (<1% of all banks) hold more than than half of all branches (51%).
- More than 6,100 banks (93% of all banks) have five or fewer branches. And, of these, more than 1,400 branches have just one branch.
Bank branch numbers change based on bank merger-and-acquisition activity, purchase and sale of portions of branch networks, as well as organic growth.
- Over the past year, the vast majority of banks (83%) did not change branch numbers.
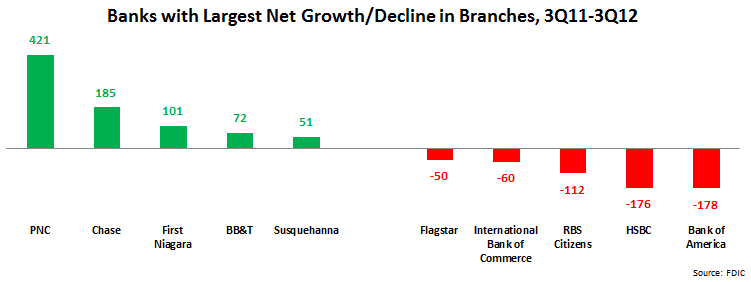
- 548 banks (8% of all banks) grew their networks by a total of 2,359 branches. PNC had the largest growth (+421 branches), largely due to its acquisition of RBS Bank as well as an Atlanta branch network from Flagstar Bank. Chase also had strong growth (+185 branches), driven by organic growth in key expansion markets like California and Florida.
- 609 banks (9% of the total) reduced their branch networks by a total of 3,092 branches. Aside from bank sales/closures, the bank with the largest decline was Bank of America, which is in the process of cutting its branch numbers by 10-15%.
Even following the reduction in branch numbers, there are almost 98,000 bank branches in the U.S., so clearly the branch channel is not going away anytime soon. However, more and more customers are gravitating to self-service electronic channels for their everyday banking needs, so a reassessment of branches’ traditional role is needed. At the same time, branches have untapped potential as sales, advice and marketing channels. The following are some key areas that banks need to focus on to both right-size their branch networks and equip these branches to realize their full sales, service and marketing potential:
- Network density. Banks will need to determine optimal branch density in key markets, in order to maintain a significant physical presence, and deter competitive market entry, while avoiding significant overlap between branch catchment areas.
- Branch size. Less traffic in branches will necessitate smaller branches in some markets. Some banks are already creating a variety of branch formats to reflect different market opportunities (as defined by market profiling that covers information like the number/projected growth of people and businesses within a radius of the branch, the bank’s overall strength in the market, as well as competitive intensity).
- Branch design. The design and layout should reflect branches’ new sales and advisory role, with less space for teller counters, and a layout more conducive to staff-customer face-to-face interaction. Recognizing that branches play an important branding and PR role for the banks, many banks are redesigning branches to convey a more customer-friendly image and promote connections with the local community.
- Staffing. Again, the changing role of the branch will mean that there will a reduced need for tellers with a greater role for specialists, such as mortgage bankers, investment advisors and small business bankers. Staff training and support tools will need to reflect their new roles in the branch.
- Technology and channel integration. As banks change the design and staffing of branches, they are incorporating technology to showcase new products and services, connect with remote staff (e.g., using videoconferencing in the branch to connect to financial advisors), and promote other bank channels (Bank of America is using QR codes in teller counters to enable customers to download its mobile banking app.)