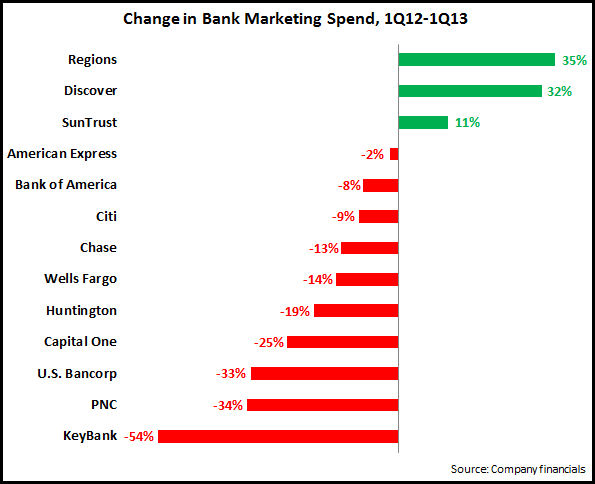
A study of the financial reports for 13 leading U.S. financial institutions reveals that 10 of these FIs reported y/y decreases in their advertising/marketing spending in the first quarter of 2013, with 7 of these banks reporting double-digit percentage decreases.
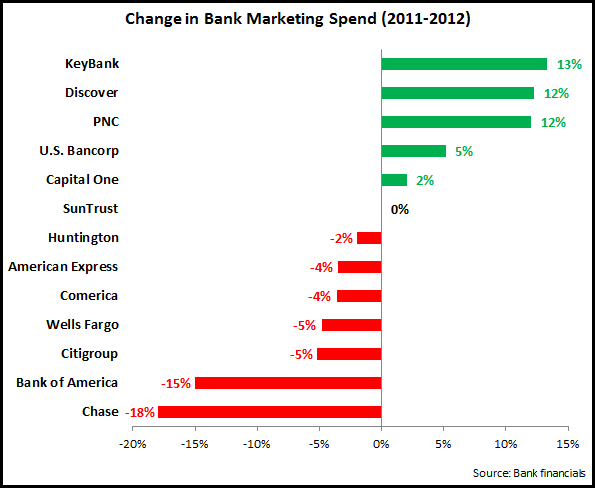
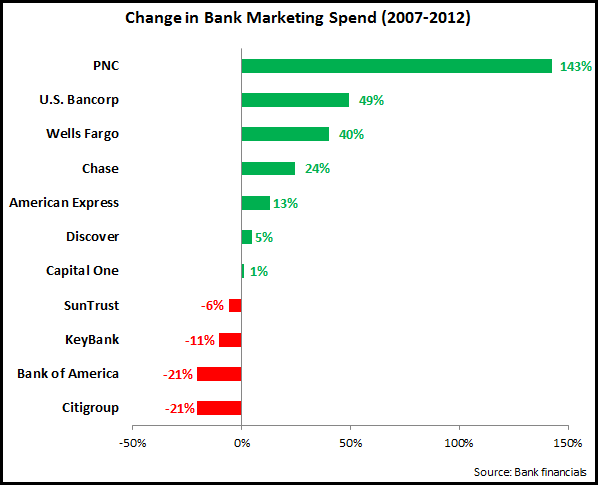
Much of this is driven by bank-wide cost-cutting initiatives, with marketing typically one of the expense line items that is most susceptible to cuts. However, it is important not to take one quarter’s worth of data as a trend. This is particularly true for bank marketing spending, which fell significantly following the financial crisis in 2008, but recovered somewhat from 2010. A recent EMI blog showed that 7 of 11 leading U.S. banks increased their marketing spend between 2007 and 2012. For example, PNC reported a strong decline in marketing spending between 1Q12 and 1Q13, but this followed a very strong rise in spending from 2007 to 2012.
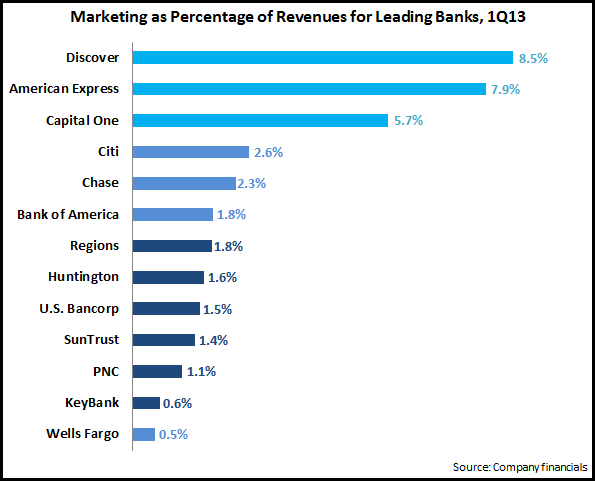
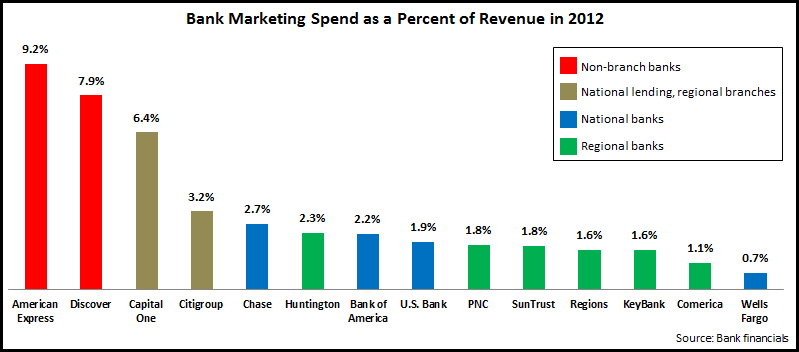
Another way to study bank marketing spend is to look at marketing spend intensity, which we define as marketing spend as a percentage of revenues.
The chart above reveals that in terms of marketing spend intensity, there are three distinct segments:
- Current (Discover and American Express) and former (Capital One) credit card monolines. In particular, Discover and American Express have limited banking operations, so remain quite dependent on their credit card business, which tends to have higher marketing spending than other financial services. In addition, Discover and American Express lack branch networks, so they need to have higher levels of advertising spend to maintain strong brand awareness.
- National banks (Citibank, Chase, and Bank of America), which typically devote 2-3% of revenues on marketing. These banks tend to have higher advertising to support their brands nationwide. In addition, these banks have large credit card operations. An exception is Wells Fargo, which spends only 0.5% of revenues on marketing. Wells Fargo has a national branch presence, but has a limited credit card business (unlike the other banks, it only markets credit cards to existing bank customers).
- Regional banks, who spend 1-2% of revenues on marketing.
Finally, it is difficult to prove a correlation between marketing spending and bank growth, as many factors influence customer acquisition and revenue growth. It is worth noting that banks continue to struggle to generaterevenue growth (7% of the 13 banks reported revenue declines between 1Q12 and 1Q13). However, the three banks with the highest marketing intensity (Discover, American Express and Capital One) were among the 6 banks that did generate y/y revenue growth.