A survey of SaaS business executives recently published by Pacific Crest (results available free here) reveals some interesting information about the profiles of higher-growth companies.
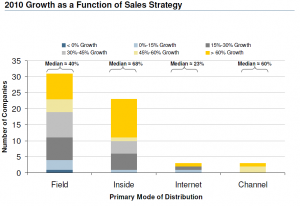
In their graph below, we can see that while the greatest number of SaaS companies use a field-based sales strategy, those that use inside sales that are actually growing the fastest—on average, almost 75% faster than the field sales companies. (Growth is defined as year-over-year change in revenue.)
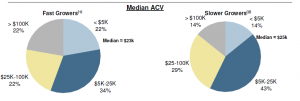
The complement to this graph is the one below, which shows that the Fast Growers (>45% growth) have lower customer acquisition costs. This differentiation is undoubtedly driven in part by the use of an inside sales force.
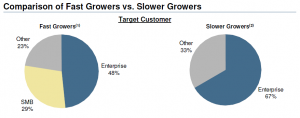
The final piece of the puzzle is revealed in the following graph. This slice of the survey data shows that Slower Growers are much more focused on Enterprise customers. Fast Growers, on the hand, balance their Enterprise sales with a healthy dose of SMB sales.
Of course, this data shouldn’t be read as an indictment of SaaS businesses that use field sales to sell mostly to the Enterprise; there are highly successful examples of such businesses. Instead, the data serves to highlight the achievement of those Fast Growers, and I hypothesize that effective marketing has played a key role in their success. It isn’t easy selling through an inside sales force to SMB; relationships are difficult to build over the phone and SMB management is often difficult to reach. Success, then, becomes a numbers game: Maximize leads (with a focus on inbound), and optimize conversions by creating tools to move prospects through the funnel. Without a highly capable marketing function, the numbers don’t add up and growth is elusive.