Several recent articles and pieces of news pertinent to robos and advisors create an interesting mosaic of the current state of human and machine advice:
- Wealthfront was valued in March at 72% of its valuation of 2 years ago.
- A J.D. Power study showed that Millennials who use self-directed platforms without much human interaction are more than 200% more likely to switch advisors than those who feel they have good communication with their advisor.
- Betterment will offer wealthier clients the ability to directly manage their accounts at a more granular level.
The image created by these items depicts the struggles in the advisory business to settle on a clear, promising strategy for integrating advice channels.
The Limits of Disruption
When robos appeared on the scene several years ago, they were heralded as the future of wealth management, a democratizing blow for the industry, and a mortal assault on traditional financial advice. Any who have seen the hype machine movie before won’t be surprised that none of those things turned out to be true. In the real world, the biggest “robos” in terms of assets are those of Vanguard and Schwab that operate as hybrids while the “pure play” B2C robos have struggled to accumulate assets and breakeven on customer acquisition costs.
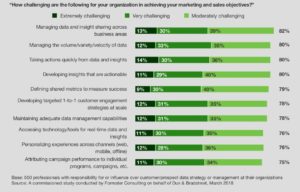
The reason for this discrepancy between reality and hype is simple: Irrational as it may sometimes be, most people want humans involved in their financial planning. A 2016 survey conducted by EMI and Boston Research Technologies showed not only that most want human involvement, but also that those who were more open to algorithm-driven investing didn’t neatly map to pre-conceived demographic categories. The bottom line is that you can’t will customers and prospects into following your vision for a service offering. Moreover, making assumptions about their behavior based on intuition and truism doesn’t create a strong foundation for success.
Changing Perspectives
The truth is that the majority of customers want a hybrid model. Many of the leading wealth managers understand this and have implemented or will implement various forms of hybrid offerings. In fact, as I mentioned earlier, the largest robos are actually those launched by existing wealth managers Vanguard and Schwab.
But any business heading down the hybrid path needs to recognize that their old models of and assumptions about client management and messaging will likely need to change. Specifically:
- If portfolio management is outsourced to machines, it becomes a commodity and value must be defined in terms of relationships and communication—an idea that has been around for some time but which has not gained universal acceptance because it is hard to execute.
- If you are advocating for clients to use your automated platform, you need to recognize that you are now responsible for their adoption of and satisfaction with the investment management software. Firms and their advisors need to be ready to assist clients onboard, answer their questions, and help them realize the full value of the software.
- Pushing the wrong clients towards a robo solution is a lose-lose situation that will cost time and assets. Firms and their advisors need to have ways of identifying where clients are likely to fall on the spectrum of interest in and comfort with automated portfolio management, recognizing that age and net worth will likely not be great proxies.