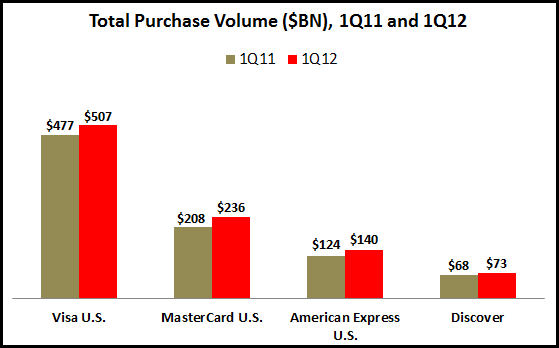
With MasterCard and Visa reporting quarterly financials in recent days, we now have a fuller picture of purchase volume trends for the main U.S. card networks. Each reported relatively strong year-on-year growth in U.S. card spending, led by MasterCard (+13%) and American Express (+12%).
It is notable that Visa and MasterCard are following different paths in growing purchase volume. Visa, which has been the dominant debit card issuer, is reporting continued slower growth in debit card purchase volume. This is due to some debit card portfolios switching to MasterCard, as well as the impact of the Durbin Amendment, and has resulted in Visa’s credit card growth outstripping its debit card growth for the past three quarters.
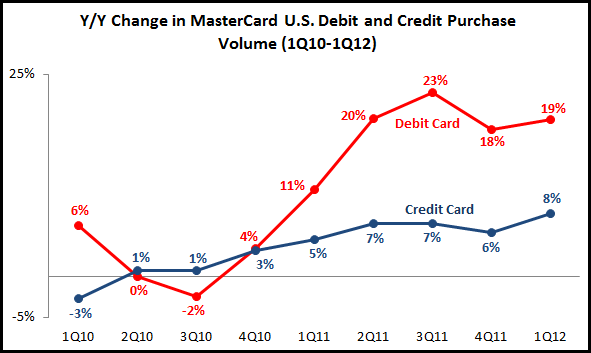
In contrast, MasterCard has reported accelerating U.S. debit card purchase volume growth. Credit card volume growth has also accelerated, but continues to trail debit card volume.
American Express has consistently recorded double-digit volume growth as it follows its spend-centric approach. Discover also reported strong growth in 2011, but this has trailed off in recent quarters.
During this period of strong purchase volume growth for both credit cards and debit cards, credit card outstandings have continued to decline, emphasizing the transition in the credit card sector from a lend-centric to spend-centric orientation. Many leading U.S. credit card issuers are expecting outstandings to grow slightly in the coming quarters, but it is probable that purchase volume growth will continue to outstrip loan growth for the foreseeable future.
Card volume growth should continue to be significantly higher than overall U.S. consumer spending growth, as consumers switch from cash and checks, with particular growth opportunities for cards in categories where they have traditionally had small shares of payment volumes.
In the longer term, card networks and issuers need to plan for new opportunities and challenges created by a changed payments landscape, characterized by demographic shifts, new payments technologies and changing shopping behavior.